Free Ransomware Decryption Tools
Hit by ransomware? Don’t pay the ransom!
Choose ransomware type
Our free ransomware decryption tools can help decrypt files encrypted by the following forms of ransomware. Just click a name to see the signs of infection and get our free fix.
- AES_NI
- Alcatraz Locker
- Apocalypse
- AtomSilo & LockFile
- Babuk
- BadBlock
- Bart
- BigBobRoss
- BTCWare
- Crypt888
- CryptoMix (Offline)
- CrySiS
- EncrypTile
- FindZip
- Fonix
- GandCrab
- Globe
- HermeticRansom
- HiddenTear
- Jigsaw
- LambdaLocker
- Legion
- NoobCrypt
- Prometheus
- Stampado
- SZFLocker
- TargetCompany
- TeslaCrypt
- Troldesh / Shade
- XData
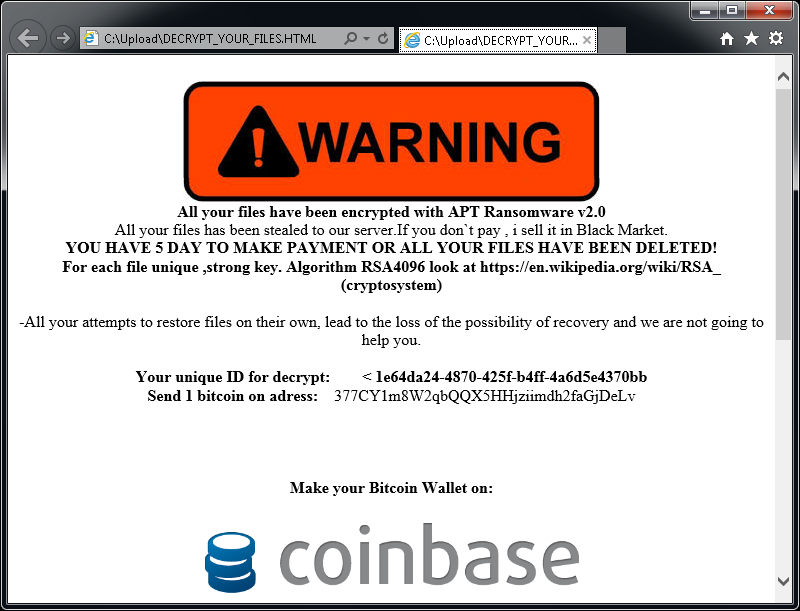
AES_NI
AES_NI is a ransomware strain that first appeared in December 2016. Since then, we’ve observed multiple variants, with different file extensions. For encrypting files, the ransomware uses AES-256 combined with RSA-2048.
The ransomware adds one of the following extensions to encrypted files:
.aes_ni
.aes256
.aes_ni_0day
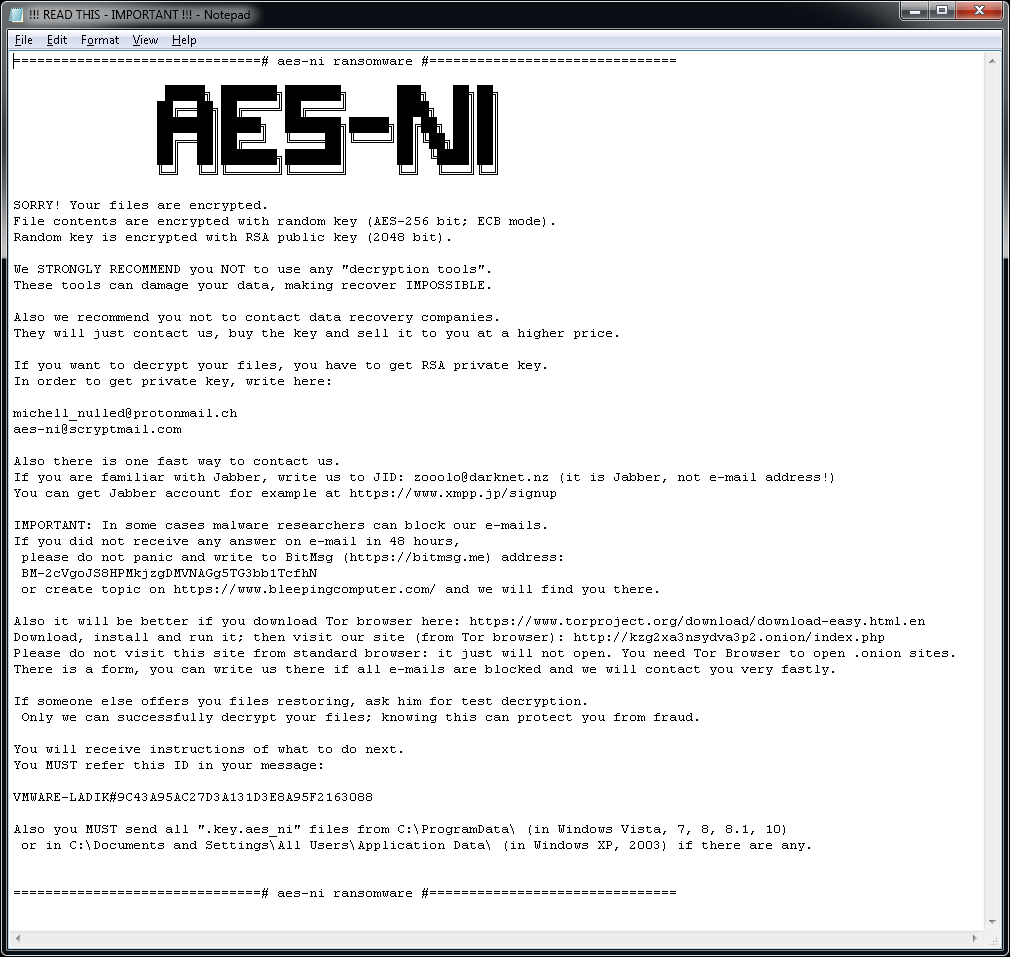
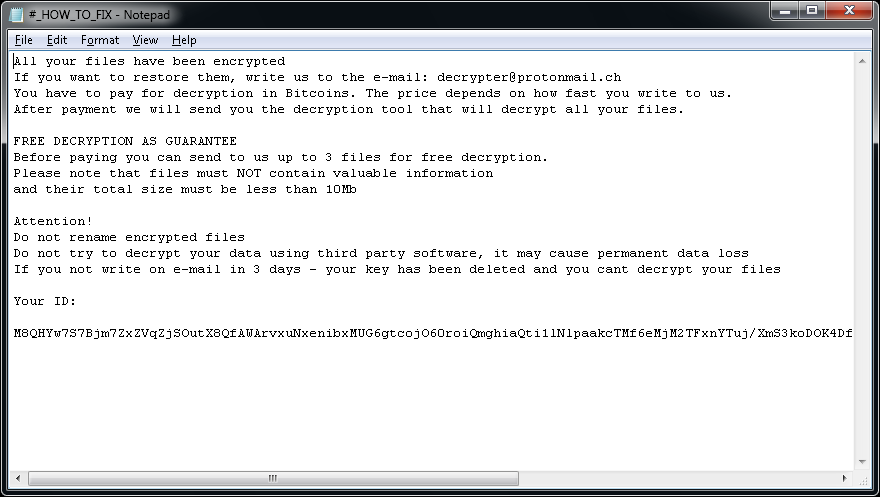
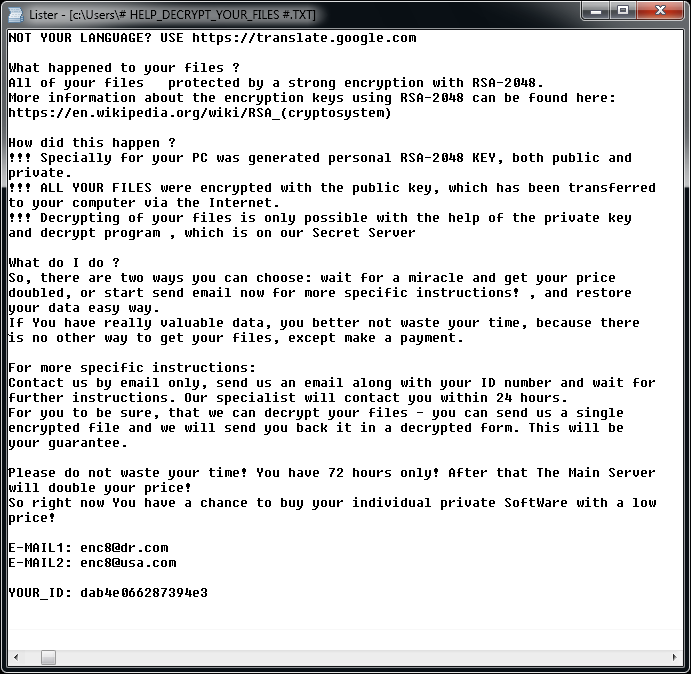
In each folder with at least one encrypted file, the file "!!! READ THIS - IMPORTANT !!!.txt" can be found. Additionally, the ransomware creates a key file with name similar to: [PC_NAME]#9C43A95AC27D3A131D3E8A95F2163088-Bravo NEW-20175267812-78.key.aes_ni_0day in C:\ProgramData folder.
The file “!!! READ THIS - IMPORTANT !!!.txt” contains the following ransom note:
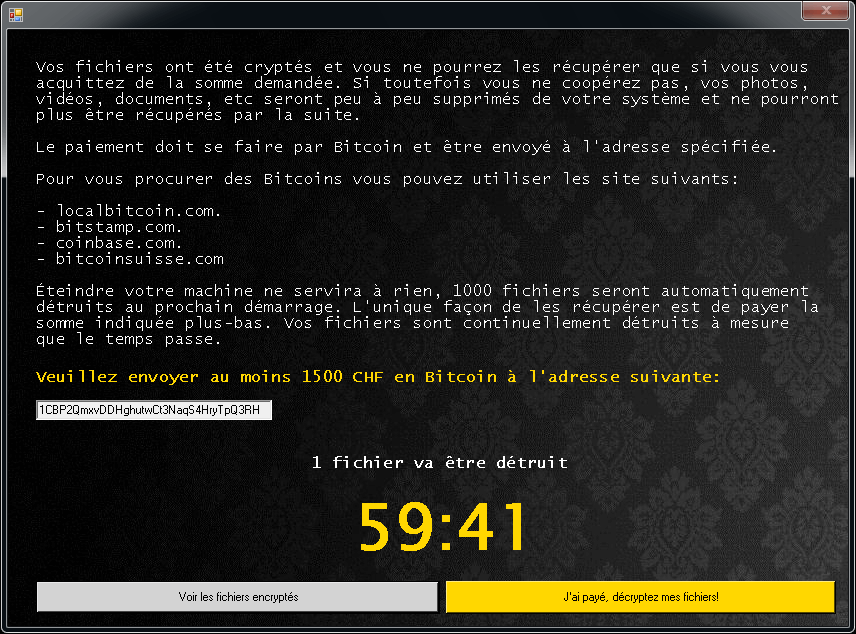
Alcatraz Locker
Alcatraz Locker is a ransomware strain that was first observed in the middle of November 2016. For encrypting user's files, this ransomware uses AES 256 encryption combined with Base64 encoding.
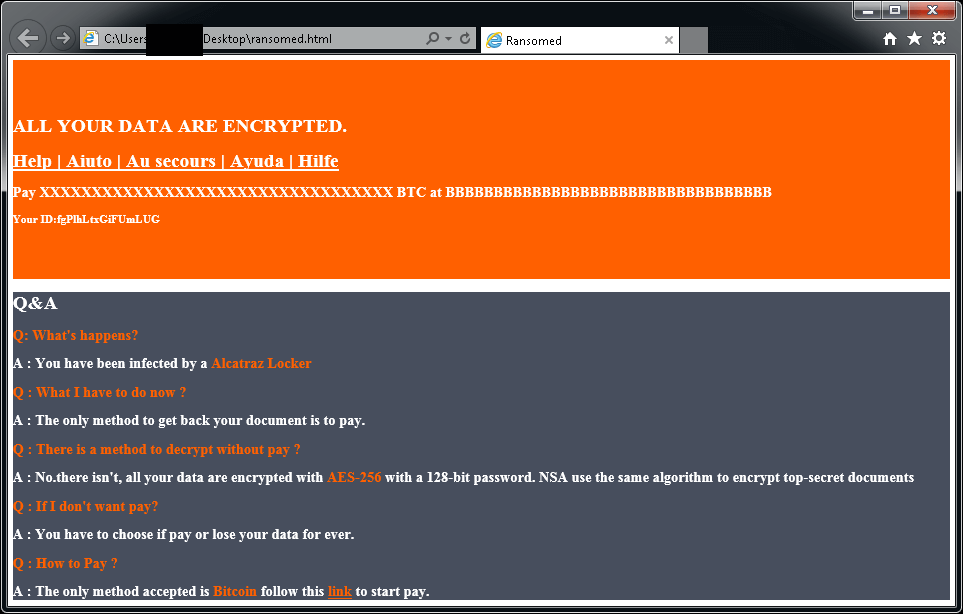
Encrypted files have the ".Alcatraz" extension.
After encrypting your files, a similar message appears (it is located in a file "ransomed.html" in the user's desktop):
If Alcatraz Locker has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
Apocalypse
Apocalypse is a form of ransomware first spotted in June 2016. Here are the signs of infection:
Apocalypse adds .encrypted, .FuckYourData, .locked, .Encryptedfile, or .SecureCrypted to the end of filenames. (e.g., Thesis.doc = Thesis.doc.locked)
Opening a file with the extension .How_To_Decrypt.txt, .README.Txt, .Contact_Here_To_Recover_Your_Files.txt, .How_to_Recover_Data.txt, or .Where_my_files.txt (e.g., Thesis.doc.How_To_Decrypt.txt) will display a variant of this message:
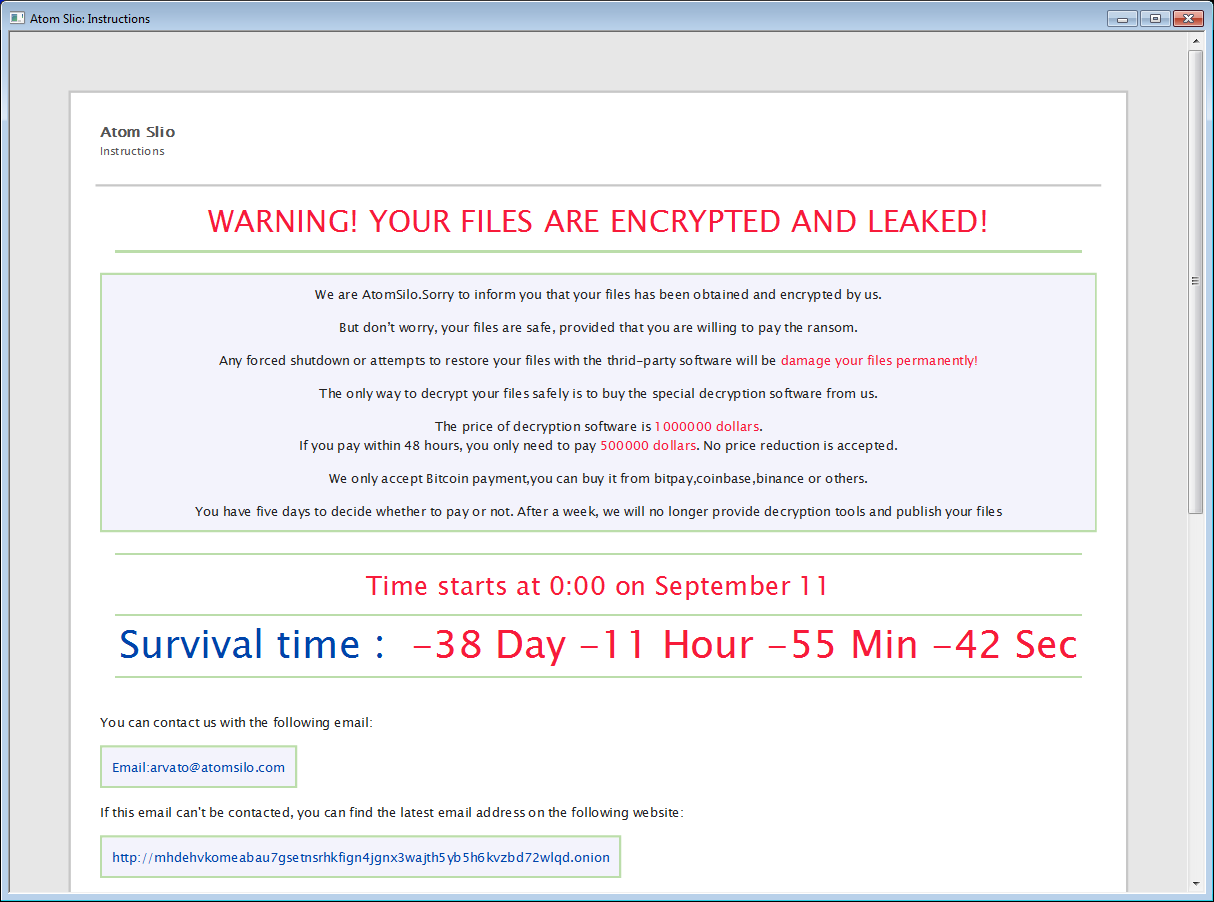
AtomSilo & LockFile
AtomSilo&LockFile are two ransomware strains analyzed by Jiří Vinopal. These two have very similar encryption schema, so this decryptor covers both variants. Victims can decrypt their files for free.
Encrypted files can be recognized by one of these extensions:
.ATOMSILO
.lockfile
In each folder with at least one encrypted file, there's also ransom note file, named README-FILE-%ComputerName%-%Number%.hta or LOCKFILE-README-%ComputerName%-%Number%.hta, e.g.:
- README-FILE-JOHN_PC-1634717562.hta
- LOCKFILE-README-JOHN_PC-1635095048.hta
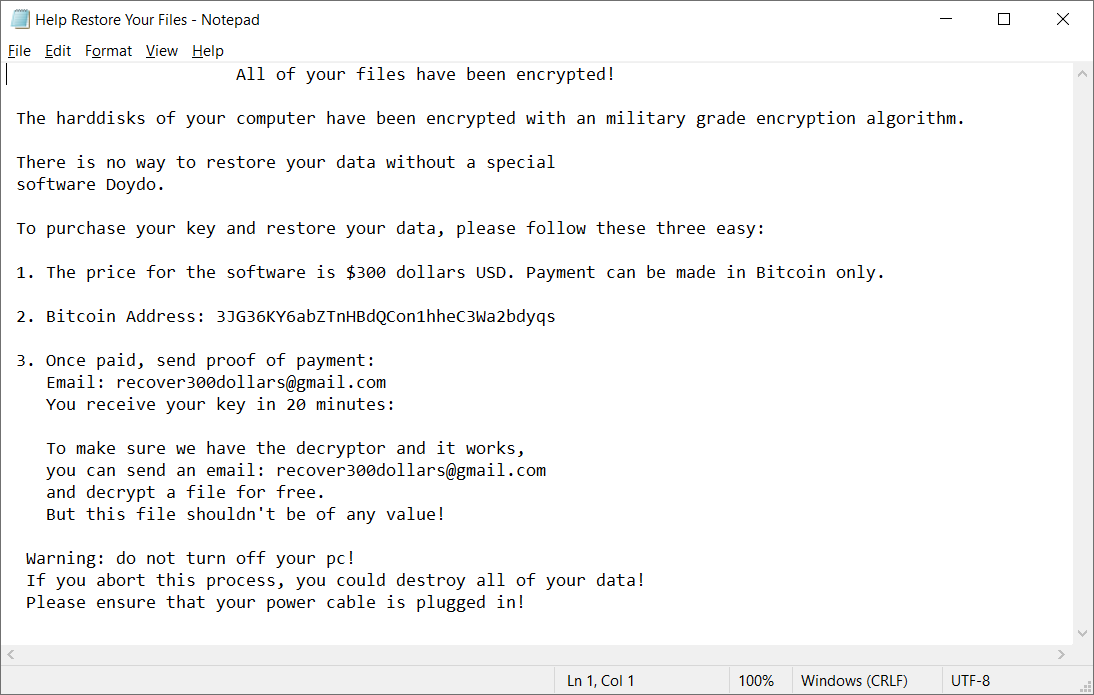
Babuk
Babuk is a Russian ransomware. In September 2021, the source code leaked with some of the decryption keys. Victims can decrypt their files for free.
When encrypting file, Babuk appends one of the following extensions to the file name:
.babuk
.babyk
.doydo
In each folder with at least one encrypted file, the file Help Restore Your Files.txt can be found with the following content:
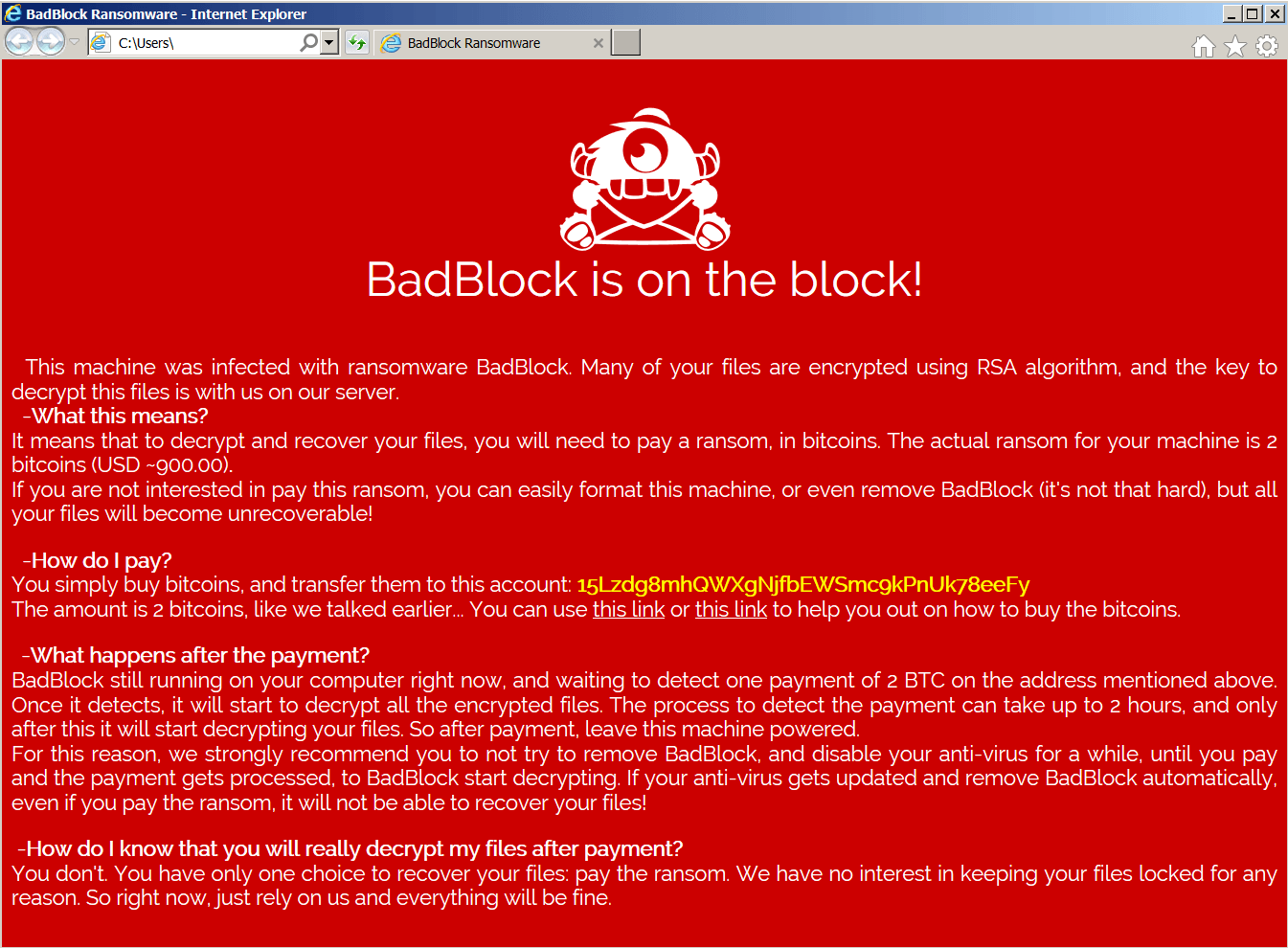
BadBlock
BadBlock is a form of ransomware first spotted in May 2016. Here are the signs of infection:
BadBlock does not rename your files.
After encrypting your files, BadBlock displays one of these messages (from a file named Help Decrypt.html):
If BadBlock has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
Bart
Bart is a form of ransomware first spotted at the end of June 2016. Here are the signs of infection:
Bart adds .bart.zip to the end of filenames. (e.g., Thesis.doc = Thesis.docx.bart.zip) These are encrypted ZIP archives containing the original files.
After encrypting your files, Bart changes your desktop wallpaper to an image like the one below. The text on this image can also be used to help identify Bart, and is stored on the desktop in files named recover.bmp and recover.txt.
If Bart has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
Acknowledgement: We'd like to thank Peter Conrad, author of PkCrack, who granted us permission to use his library in our Bart decryption tool.
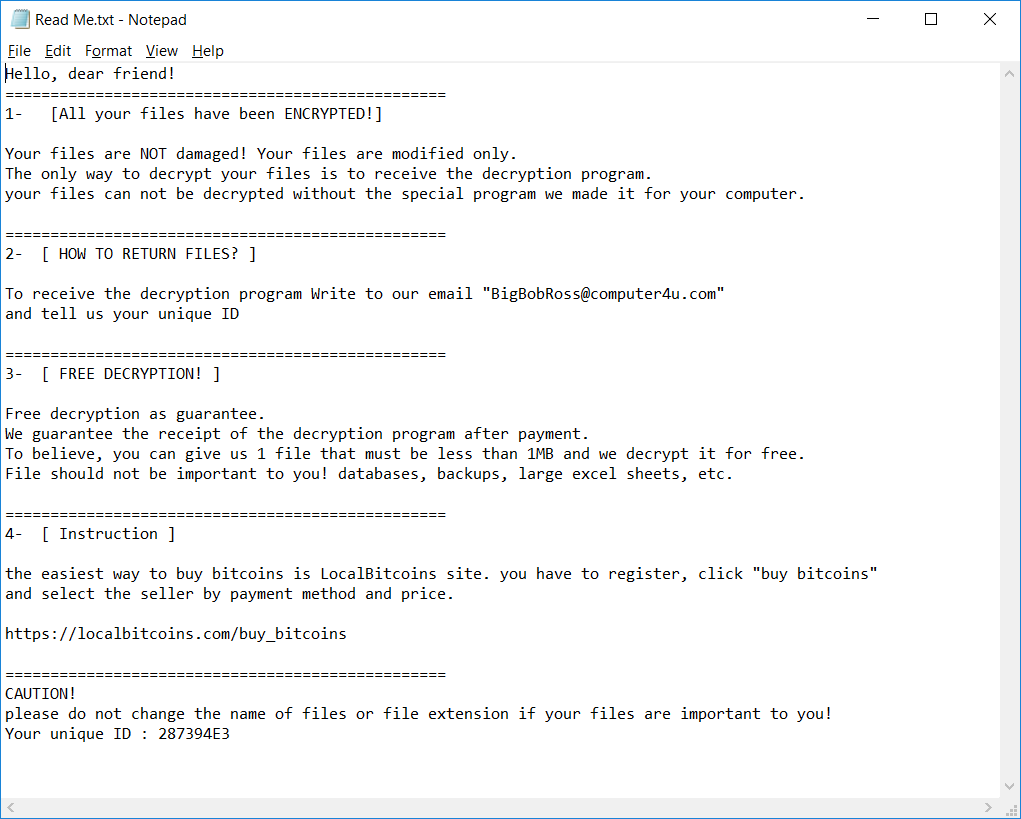
BigBobRoss
BigBobRoss encrypts user's files using AES128 encryption. The encrypted files have new extension ".obfuscated" appended at the end of the file name.
The ransomware adds the following extension: .obfuscated
foobar.doc -> foobar.doc.obfuscated
document.dat -> document.dat.obfuscated
document.xls -> document.xls.obfuscated
foobar.bmp -> foobar.bmp.obfuscated
The ransomware also creates a text file named "Read Me.txt" in each folder. The content of the file is below.
BTCWare
BTCWare is a ransomware strain that first appeared in March 2017. Since then, we observed five variants, that can be distinguished by encrypted file extension. The ransomware uses two different encryption methods – RC4 and AES 192.
Encrypted file names will have the following format:
foobar.docx.[sql772@aol.com].theva
foobar.docx.[no.xop@protonmail.ch].cryptobyte
foobar.bmp.[no.btc@protonmail.ch].cryptowin
foobar.bmp.[no.btcw@protonmail.ch].btcware
foobar.docx.onyon
Furthermore, one of the following files can be found on the PC
Key.dat on %USERPROFILE%\Desktop
1.bmp in %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming
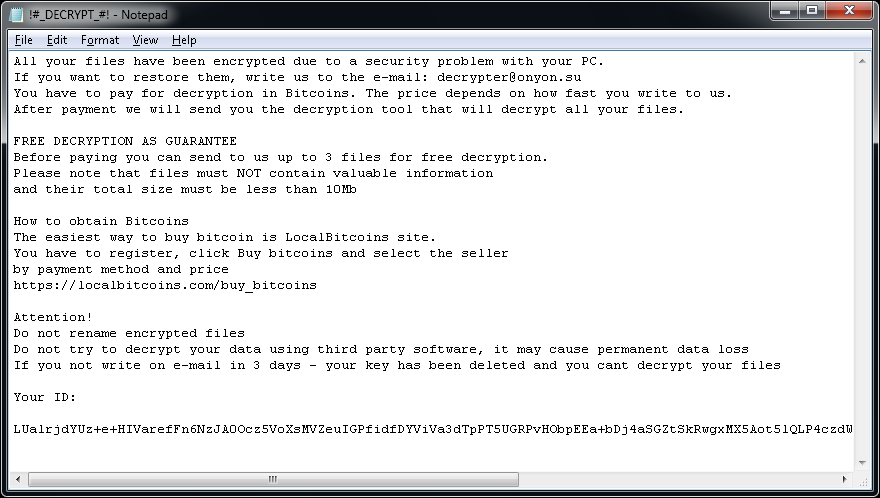
#_README_#.inf or !#_DECRYPT_#!.inf in each folder with at least one encrypted file.
After encrypting your files, the desktop wallpaper is changed to the following:
You may also see one of the following ransom notes:
Crypt888
Crypt888 (also known as Mircop) is a form of ransomware first spotted in June 2016. Here are the signs of infection:
Crypt888 adds Lock. to the beginning of filenames. (e.g., Thesis.doc = Lock.Thesis.doc)
After encrypting your files, Crypt888 changes your desktop wallpaper to one of the following:
If Crypt888 has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
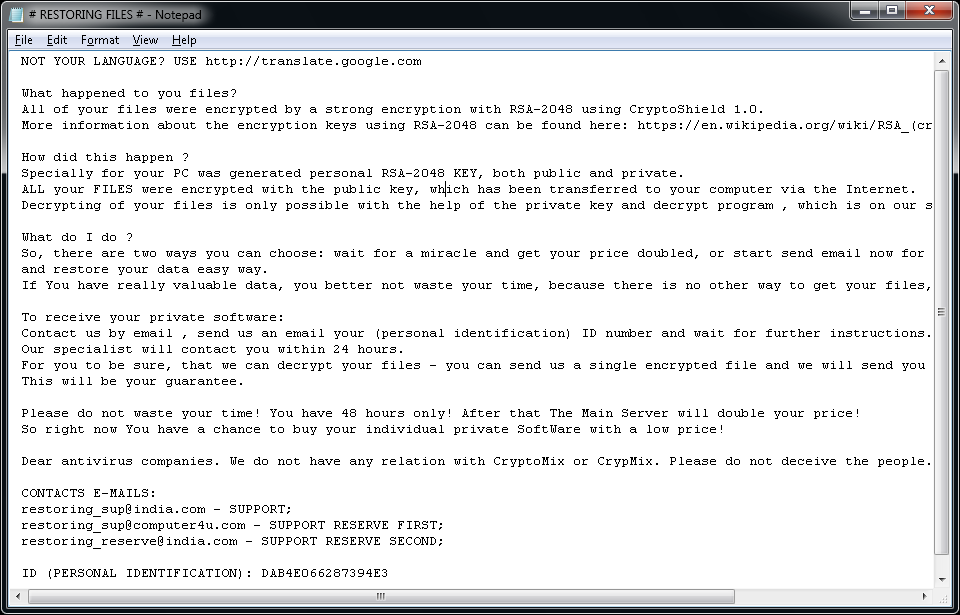
CryptoMix (Offline)
CryptoMix (also known as CryptFile2 or Zeta) is a ransomware strain that was first spotted in March 2016. In early 2017, a new variant of CryptoMix, called CryptoShield emerged. Both variants encrypt files by using AES256 encryption with a unique encryption key downloaded from a remote server. However, if the server is not available or if the user is not connected to the internet, the ransomware will encrypt files with a fixed key ("offline key").
Important: The provided decryption tool only supports files encrypted using an "offline key". In cases where the offline key was not used to encrypt files, our tool will be unable to restore the files and no file modification will be done.
Update 2017-07-21: The decryptor was updated to also work with Mole variant.
Encrypted files will have one of the following extensions: .CRYPTOSHIELD, .rdmk, .lesli, .scl, .code, .rmd, .rscl or .MOLE.
The following files may be found on the PC after encrypting files:
If CryptoMix has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
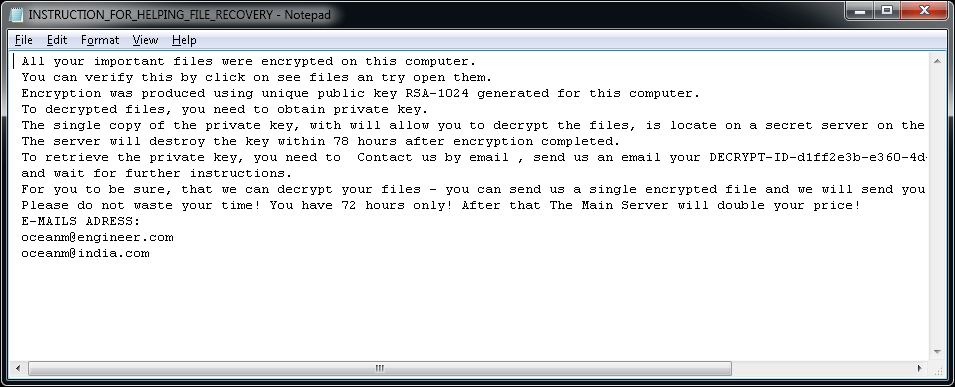
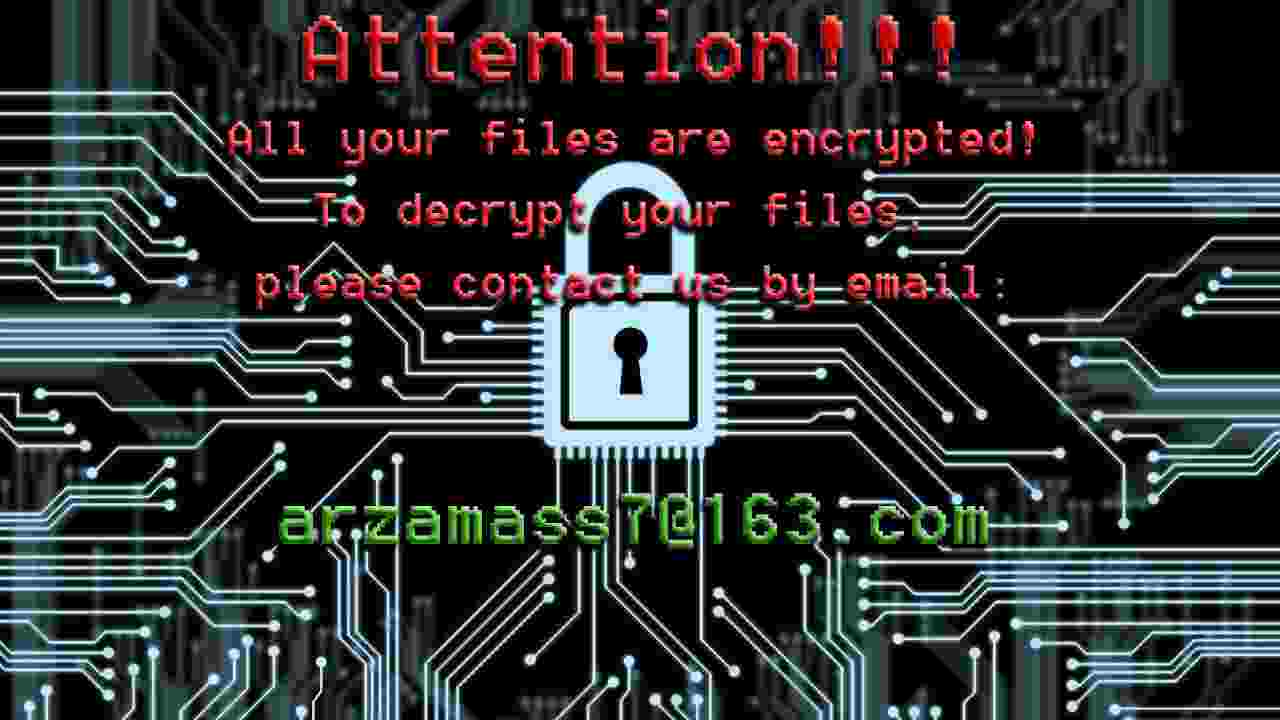
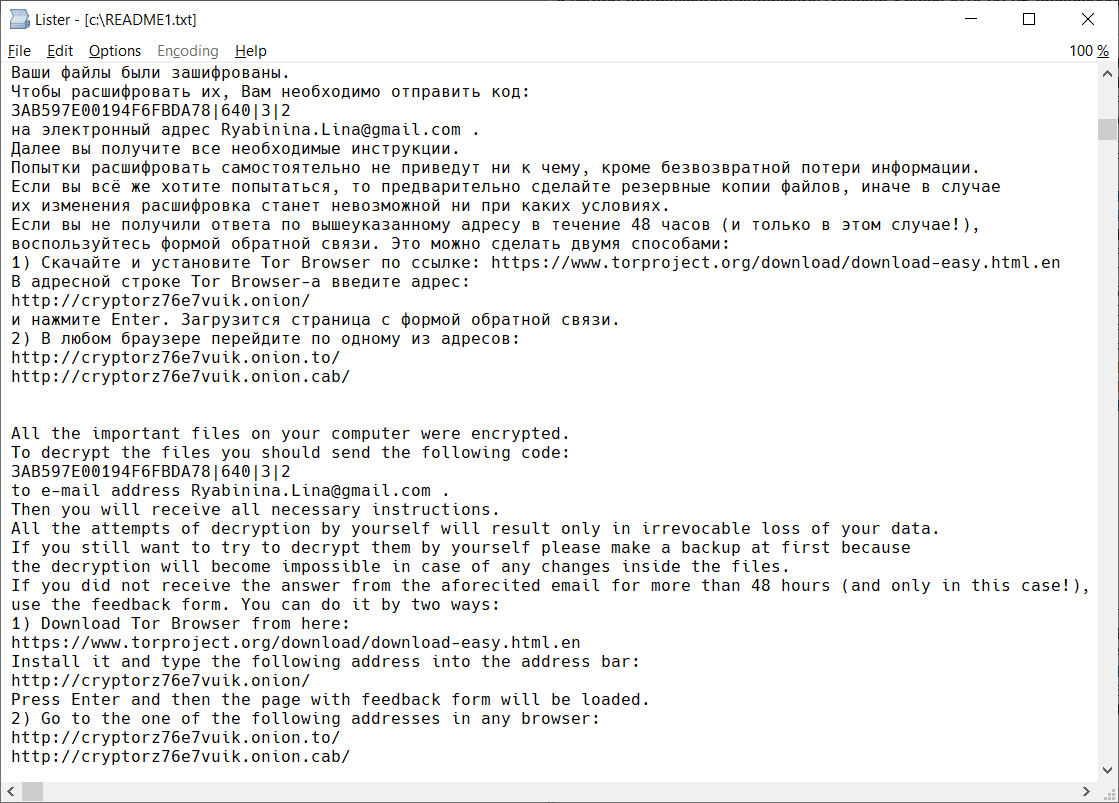
CrySiS
CrySiS (JohnyCryptor, Virus-Encode, Aura, Dharma) is a ransomware strain that has been observed since September 2015. It uses AES-256 combined with RSA-1024 asymmetric encryption.
Encrypted files have many various extensions, including:
.johnycryptor@hackermail.com.xtbl,
.ecovector2@aol.com.xtbl,
.systemdown@india.com.xtbl,
.Vegclass@aol.com.xtbl,
.{milarepa.lotos@aol.com}.CrySiS,
.{Greg_blood@india.com}.xtbl,
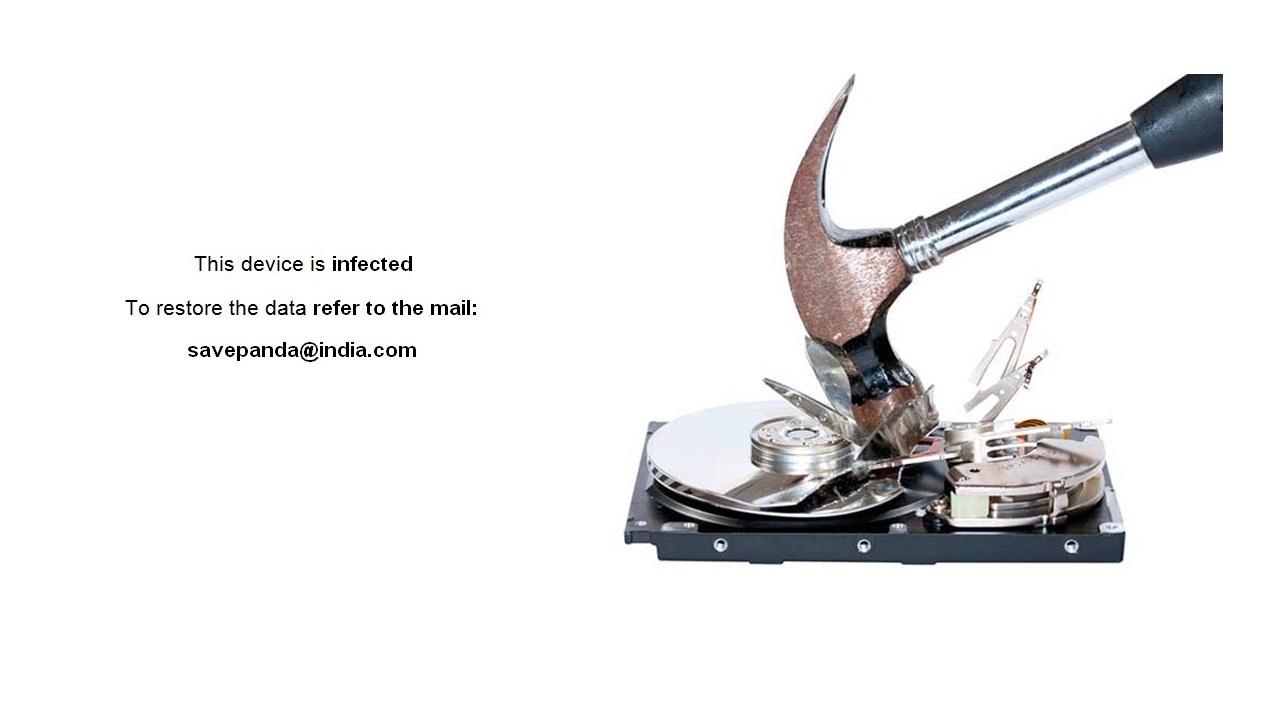
.{savepanda@india.com}.xtbl,
.{arzamass7@163.com}.xtbl,
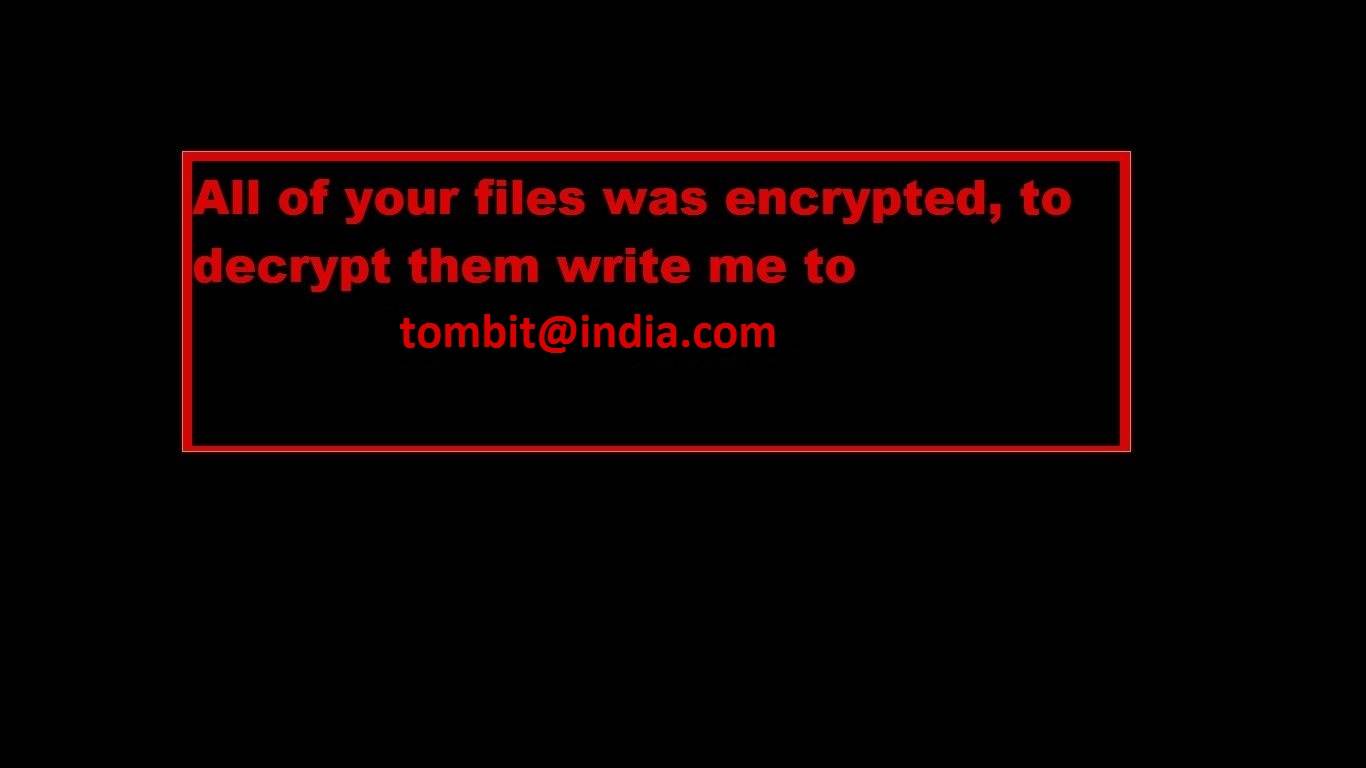
.{3angle@india.com}.dharma,
.{tombit@india.com}.dharma,
.wallet
After encrypting your files, one of the following messages appears (see below). The message is located in "Decryption instructions.txt", "Decryptions instructions.txt", "README.txt", "Readme to restore your files.txt" or "HOW TO DECRYPT YOUR DATA.txt" on the user's desktop. Also, the desktop background is changed to one of the pictures below.
If CrySiS has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
EncrypTile
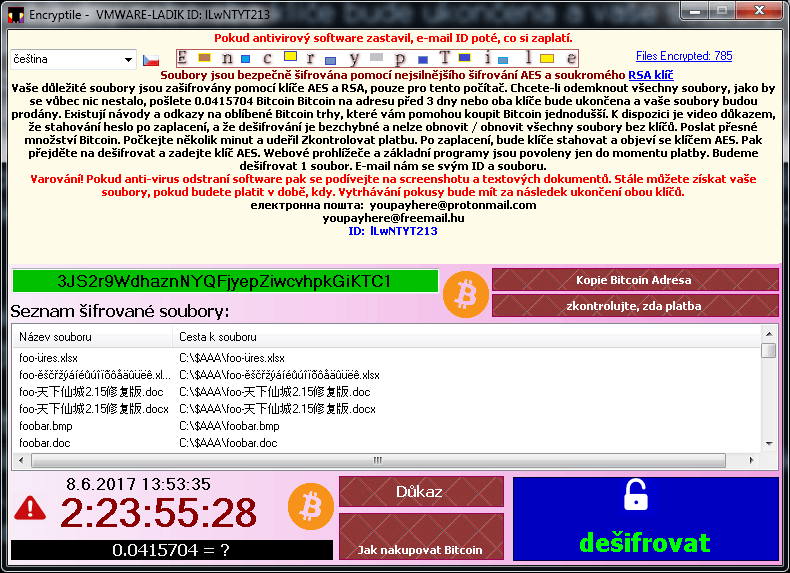
EncrypTile is a ransomware that we first observed in November of 2016. After a half-year development, we caught a new, final version of this ransomware. It uses AES-128 encryption, using a key that is constant for a given PC and user.
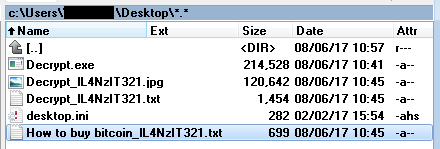
The ransomware adds the word “encrypTile” into a file name:
foobar.doc -> foobar.docEncrypTile.doc
foobar3 -> foobar3EncrypTile
The ransomware also creates four new files on user’s desktop. Names of these files are localized, here are their English versions:
While running, the ransomware actively prevents the user from running any tools that might potentially remove it. Refer to the blog post for more detailed instructions how to run the decryptor in case the ransomware is running on your PC.
FindZip
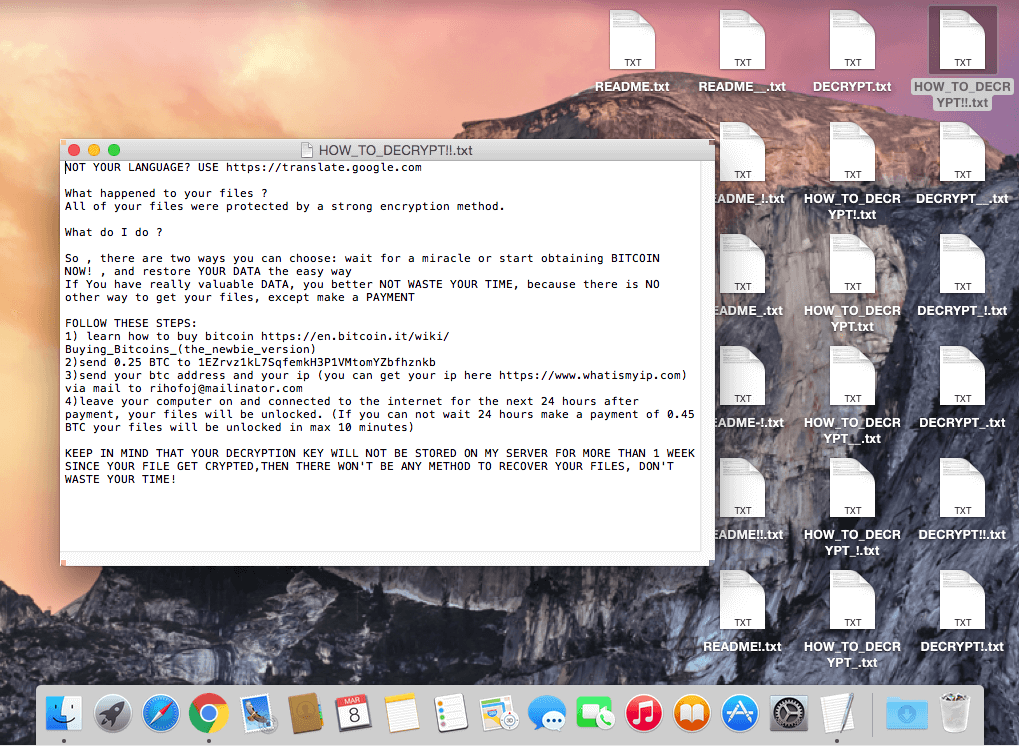
FindZip is a ransomware strain that was observed at the end of February 2017. This ransomware spreads on Mac OS X (version 10.11 or newer). The encryption is based on creating ZIP files - each encrypted file is a ZIP archive, containing the original document.
Encrypted files will have the .crypt extension.
After encrypting your files, several files are created on the user’s desktop, with name variants of: DECRYPT.txt, HOW_TO_DECRYPT.txt, README.txt. They are all identical, containing the following text message:
Special: Because AVAST decryptors are Windows applications, it is necessary to install an emulation layer on Mac (WINE, CrossOver). For more information, please, read our blog post.
If Globe has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
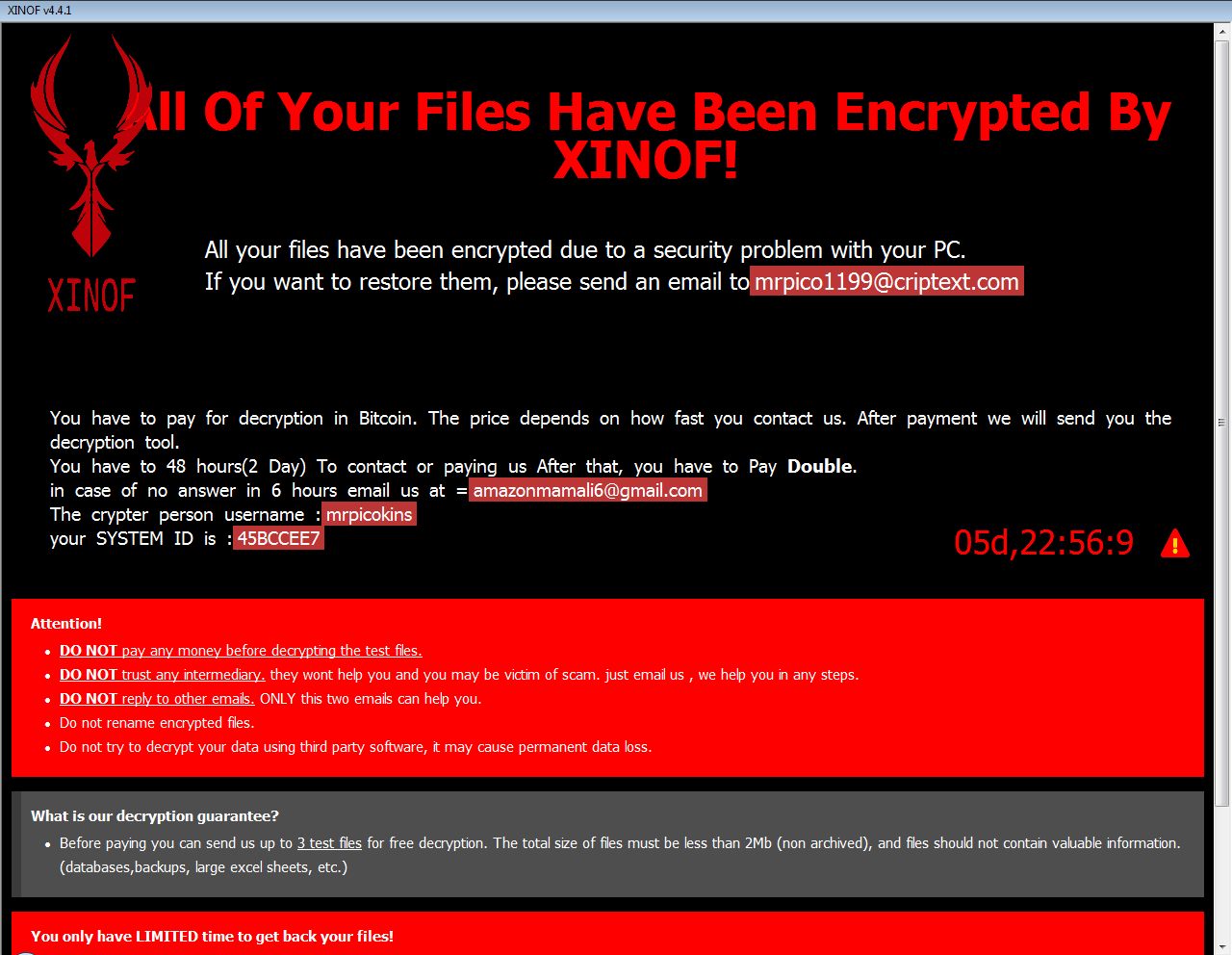
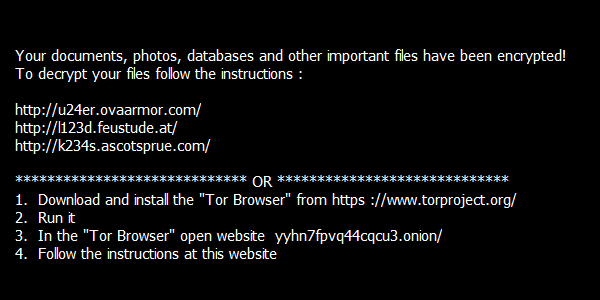
Fonix
The Fonix ransomware was active since June 2020. Written in C++, it uses three key encryption scheme (RSA-4096 master key, RSA-2048 session key, 256-bit file key for SALSA/ChaCha encryption). On February 2021, the ransomware authors shut their business down and published the master RSA key that can be used for decrypting files for free.
Encrypted files will have one of these extensions:
.FONIX,
.XINOF
After encrypting files on the victim machine, the ransomware shows the following screen:
If Fonix has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
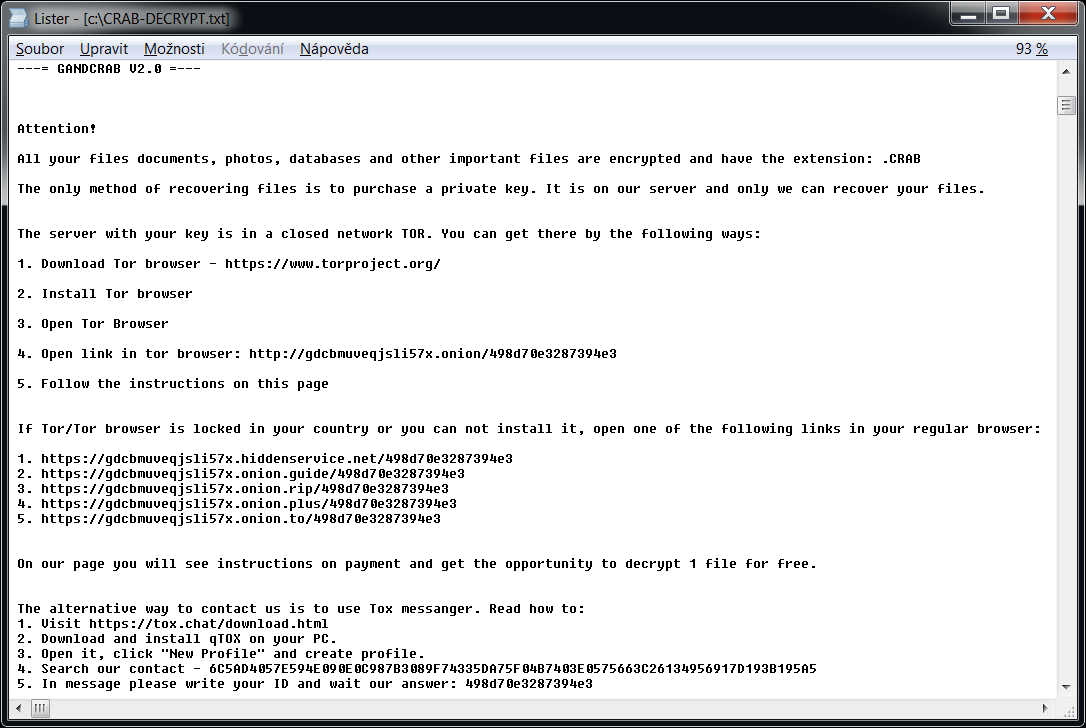
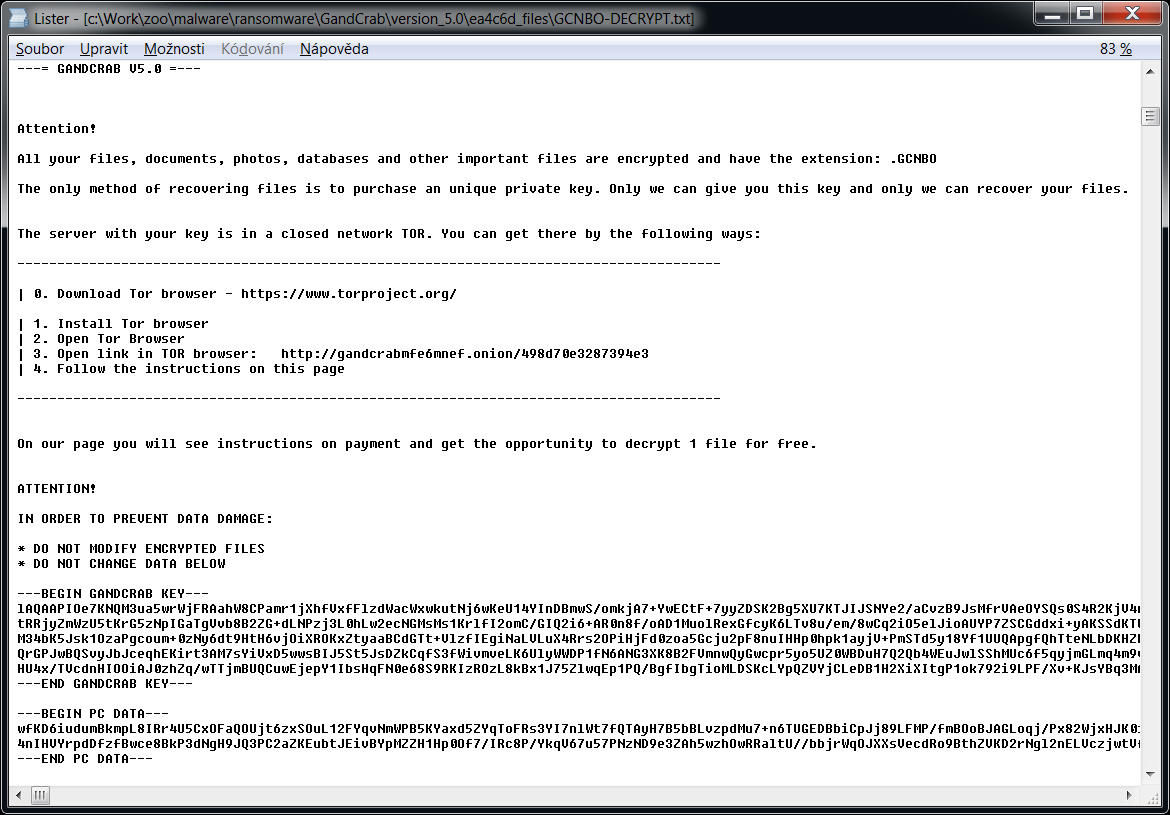
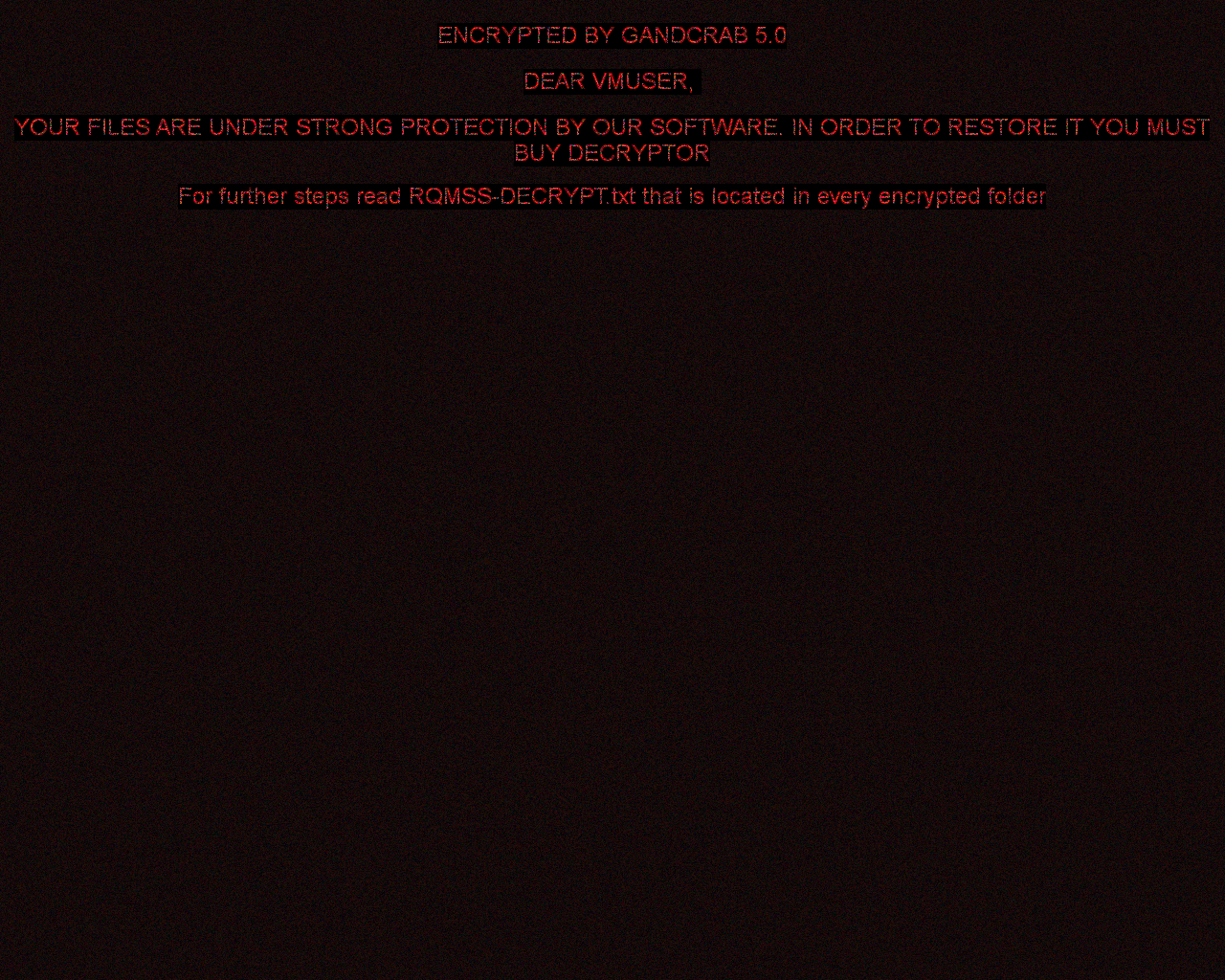
GandCrab
Gandcrab is one of the most prevalent ransomware in 2018. On 17. October 2018, Gandcrab developers released 997 keys for victims that are located in Syria. Also, in July 2018, FBI released master decryption keys for versions 4-5.2. This version of decryptor utilises all these keys and can decrypt files for free.
The ransomware adds multiple possible extensions:
.GDCB,
.CRAB,
.KRAB,
.%RandomLetters%
foobar.doc -> foobar.doc.GDCB
document.dat -> document.dat.CRAB
document.xls -> document.xls.KRAB
foobar.bmp -> foobar.bmp.gcnbo (letters are random)
The ransomware also creates a text file named "GDCB-DECRYPT.txt", "CRAB-DECRYPT.txt", "KRAB_DECRYPT.txt", "%RandomLetters%-DECRYPT.txt" or "%RandomLetters%-MANUAL.txt" in each folder. The content of the file is below.
Later versions of the ransomware can also set the following image to the user's desktop:
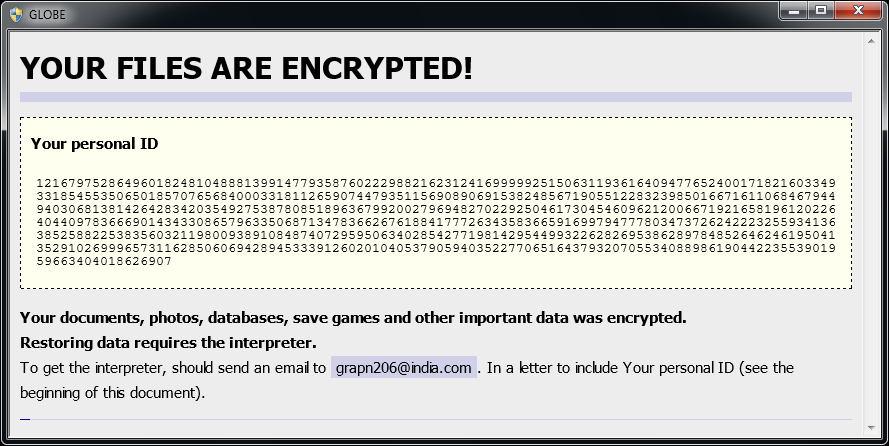
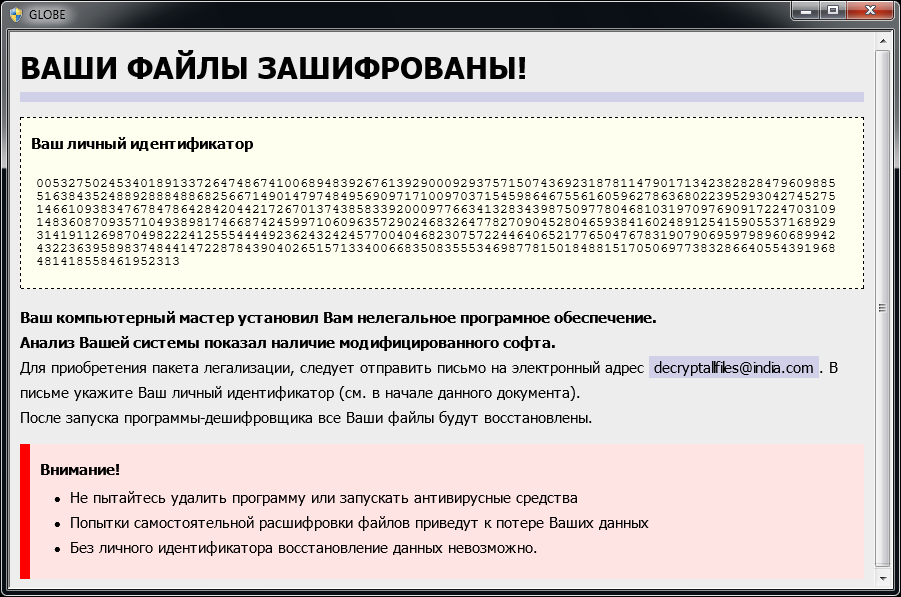
Globe
Globe is a ransomware strain that has been observed since August 2016. Based on variant, it uses RC4 or Blowfish encryption method. Here are signs of infection:
Globe adds one of the following extensions to the file name: ".ACRYPT", ".GSupport[0-9]", ".blackblock", ".dll555", ".duhust", ".exploit", ".frozen", ".globe", ".gsupport", ".kyra", ".purged", ".raid[0-9]", ".siri-down@india.com", ".xtbl", ".zendrz", ".zendr[0-9]", or ".hnyear". Furthermore, some of its versions encrypt the file name as well.
After encrypting your files, a similar message appears (it is located in a file "How to restore files.hta" or "Read Me Please.hta"):
If Globe has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
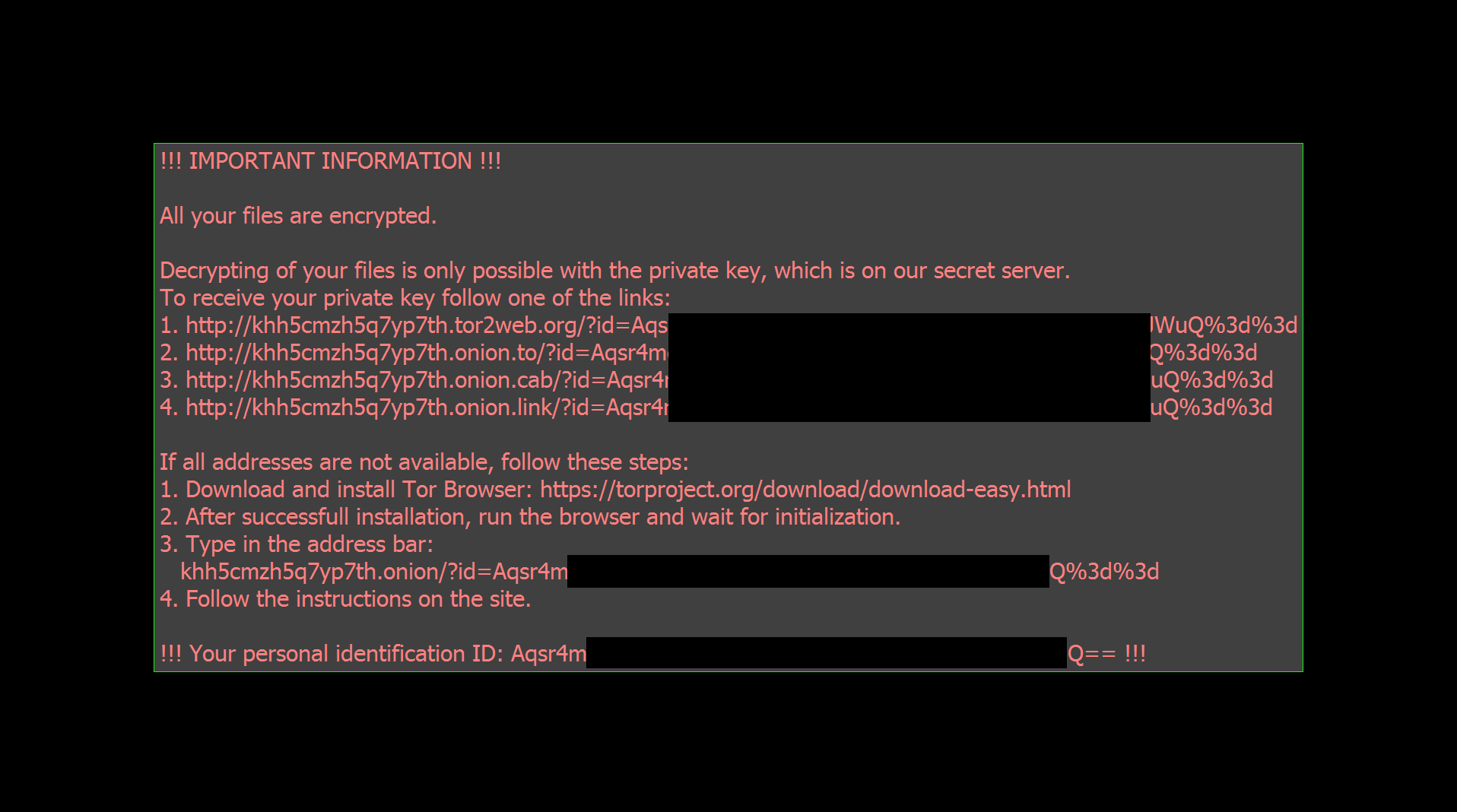
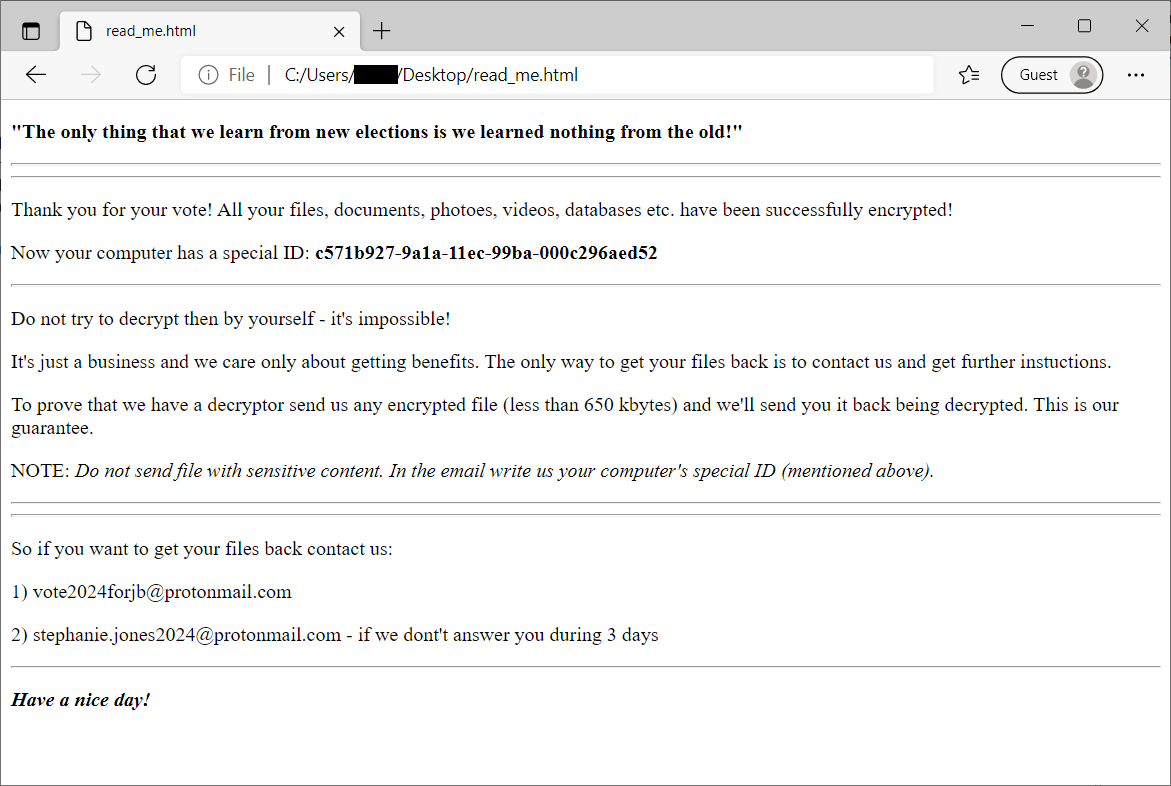
HermeticRansom
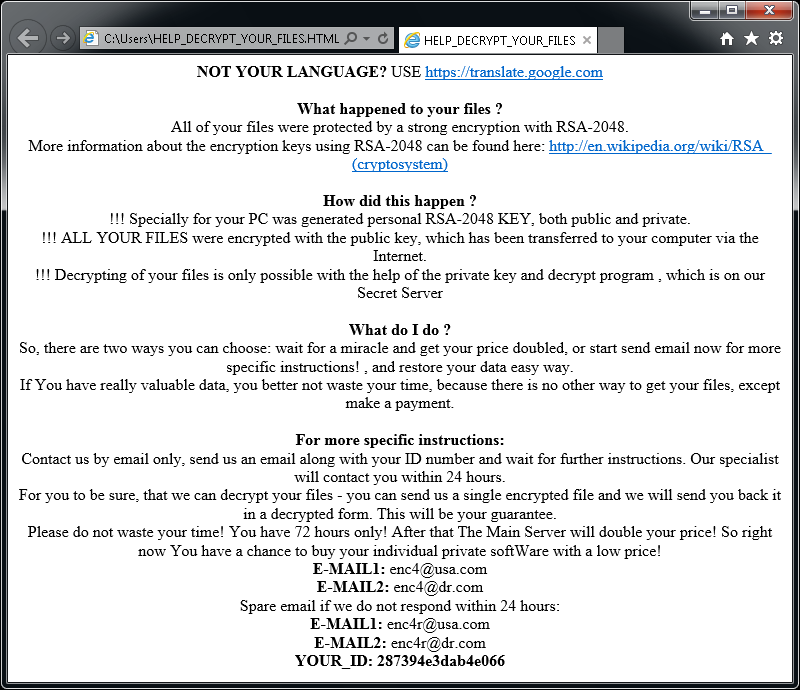
HermeticRansom is ransomware that was used at the beginning of the Russian invasion to Ukraine. It is written in Go language and encrypts files with the AES GCM symmetric cipher. Victim of this ransomware attack can decrypt their files for free.
Encrypted files can be recognized by the .[vote2024forjb@protonmail.com].encryptedJB file extension. Also, a file named read_me.html is dropped to the user's desktop (see the image below).
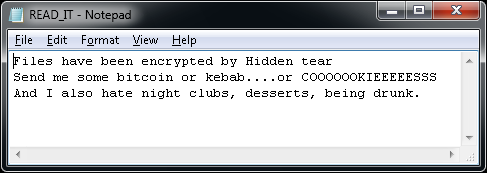
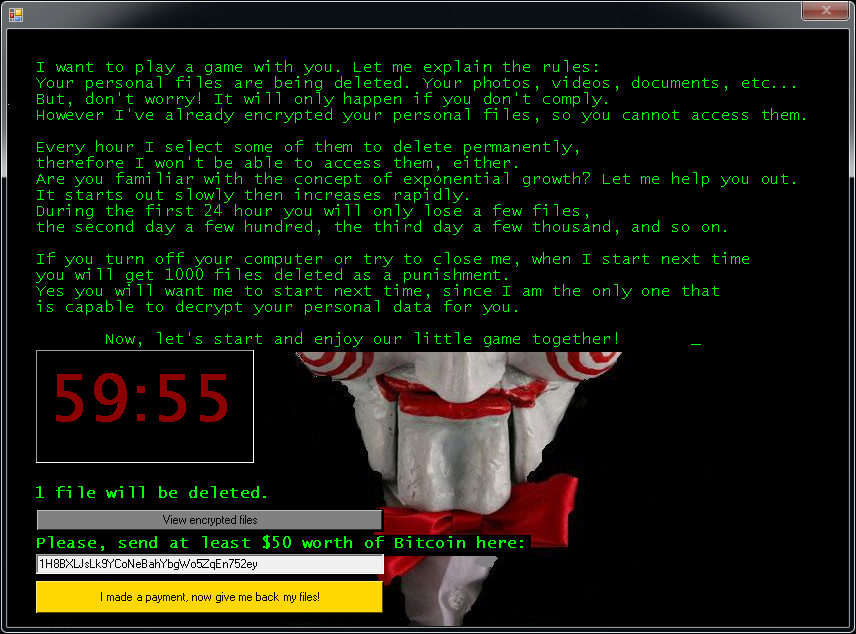
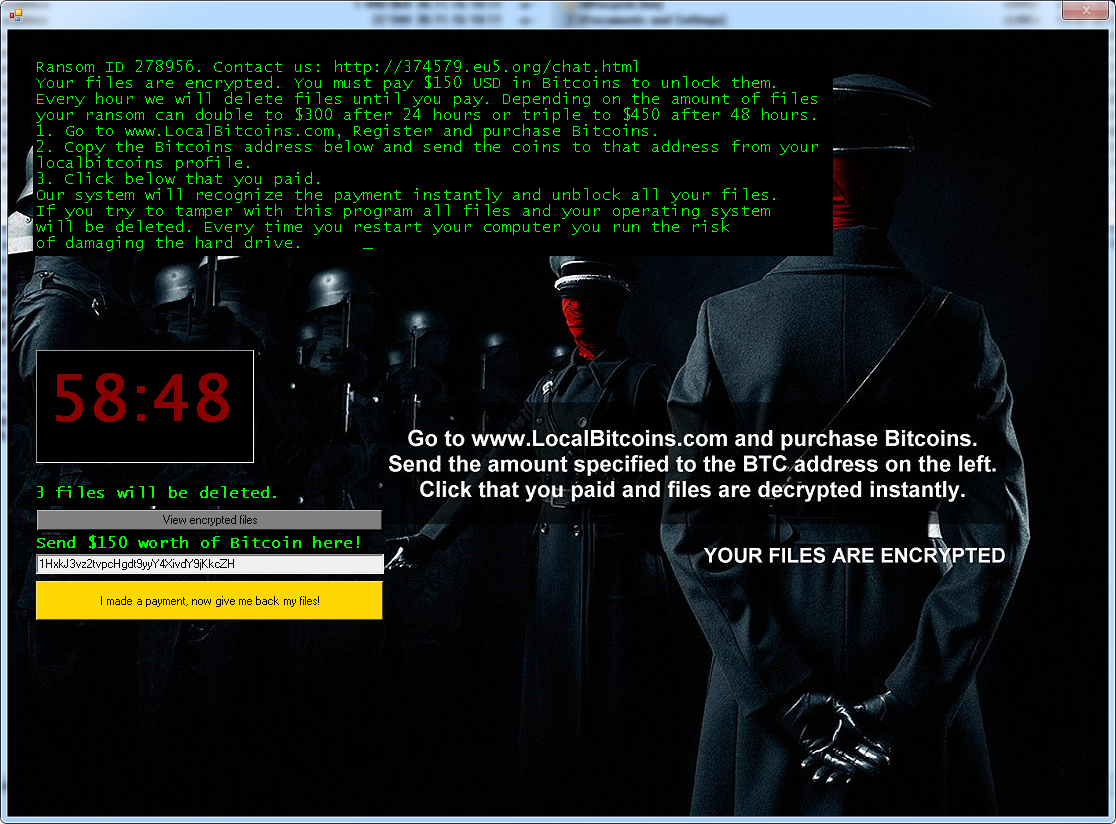
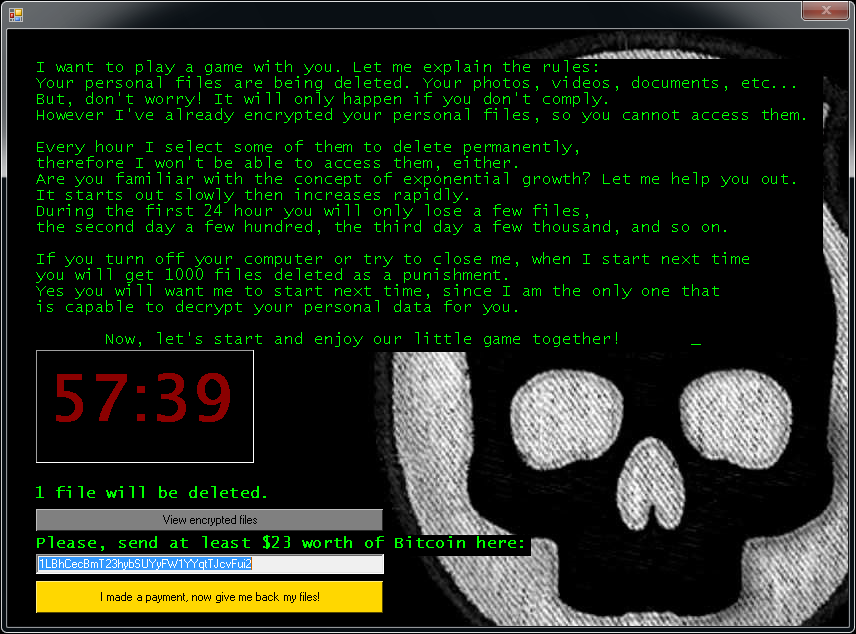
Jigsaw
Jigsaw is a ransomware strain that has been around since March 2016. It’s named after the movie character “The Jigsaw Killer”. Several variants of this ransomware use the Jigsaw Killer’s picture in the ransom screen.
Encrypted files will have one of the following extensions: .kkk, .btc, .gws, .J, .encrypted, .porno, .payransom, .pornoransom, .epic, .xyz, .versiegelt, .encrypted, .payb, .pays, .payms, .paymds, .paymts, .paymst, .payrms, .payrmts, .paymrts, .paybtcs, .fun, .hush, .uk-dealer@sigaint.org, or .gefickt.
After encrypting your files, one of the screens below will appear:
If Jigsaw has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
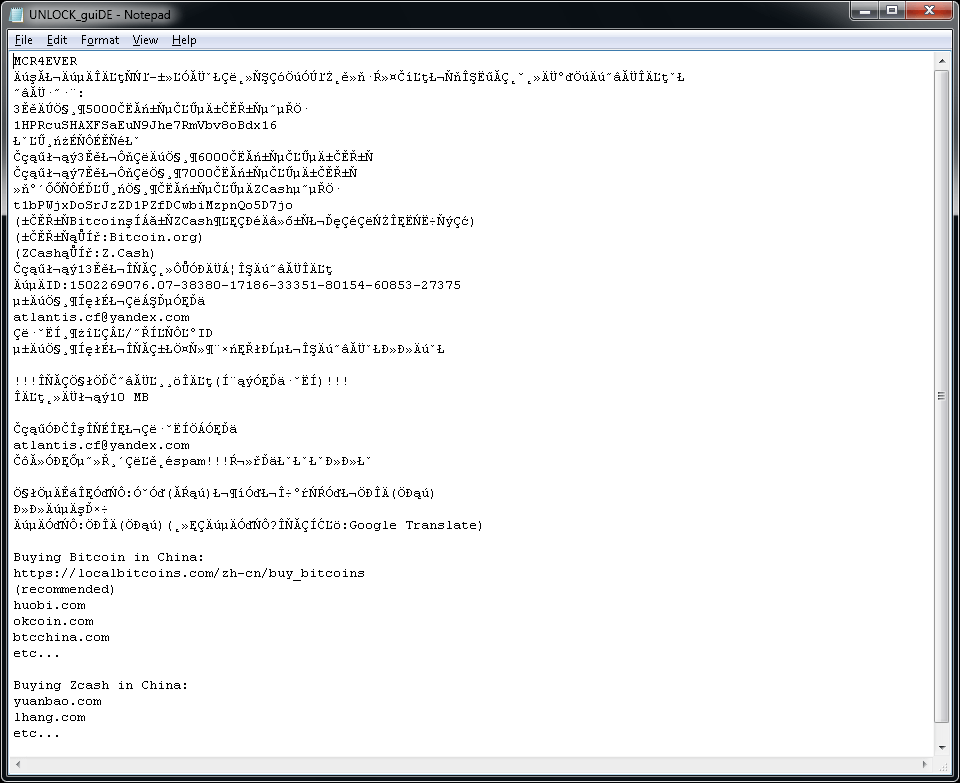
LambdaLocker
LambdaLocker is a ransomware strain that we first observed in May 2017. It is written in Python programming language and the currently prevalent variant is decryptable.
The ransomware adds the “.MyChemicalRomance4EVER” extension after a file name:
foobar.doc -> foobar.doc.MyChemicalRomance4EVER
document.dat -> document.dat.MyChemicalRomance4EVER
The ransomware also creates a text file named "UNLOCK_guiDE.txt" on the user's desktop. The content of the file is below.
Legion
Legion is a form of ransomware first spotted in June 2016. Here are the signs of infection:
Legion adds a variant of ._23-06-2016-20-27-23_$f_tactics@aol.com$.legion or .$centurion_legion@aol.com$.cbf to the end of filenames. (e.g., Thesis.doc = Thesis.doc._23-06-2016-20-27-23_$f_tactics@aol.com$.legion)
After encrypting your files, Legion changes your desktop wallpaper and displays a popup, like this:
If Legion has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
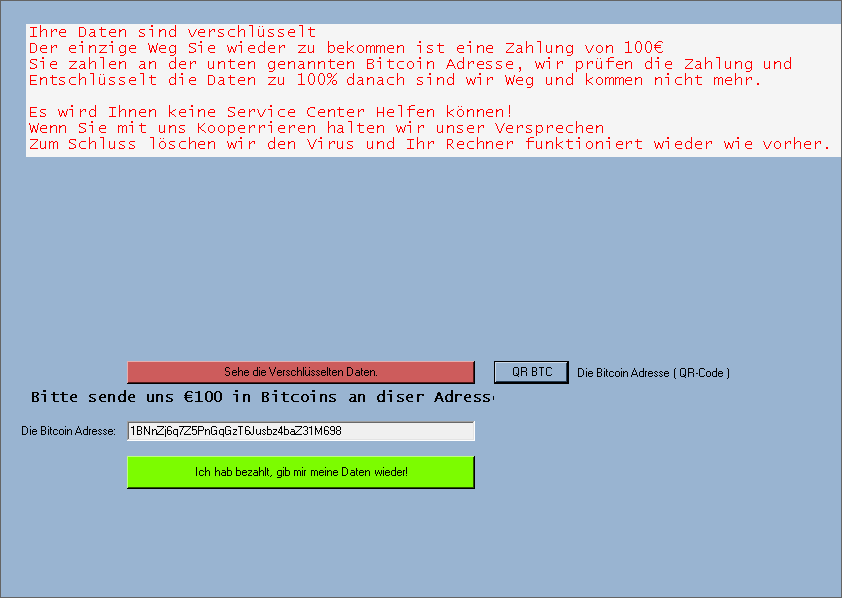
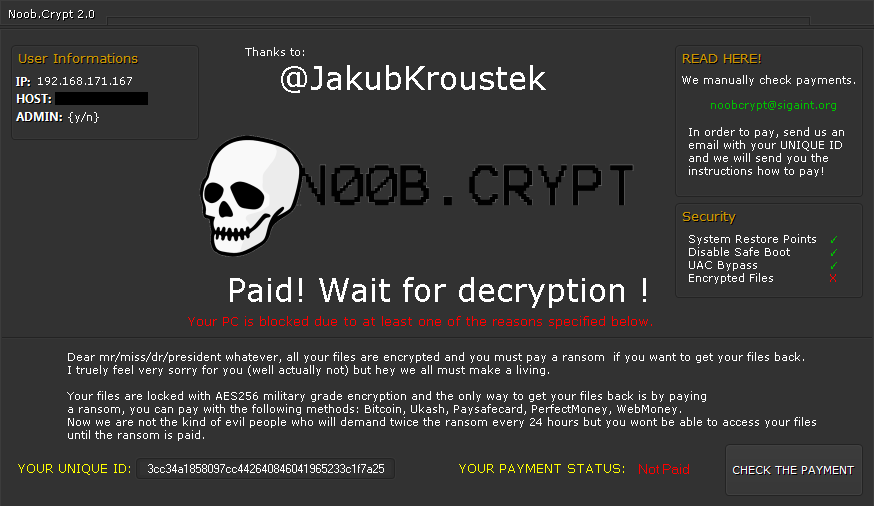
NoobCrypt
NoobCrypt is a ransomware strain that has been observed since the late July 2016. For encrypting user's files, this ransomware uses AES 256 encryption method.
NoobCrypt doesn't change file name. Files that are encrypted are unable to be open with their associated application, however.
After encrypting your files, a similar message appears (it is located in a file "ransomed.html" in the user's desktop):
If NoobCrypt has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
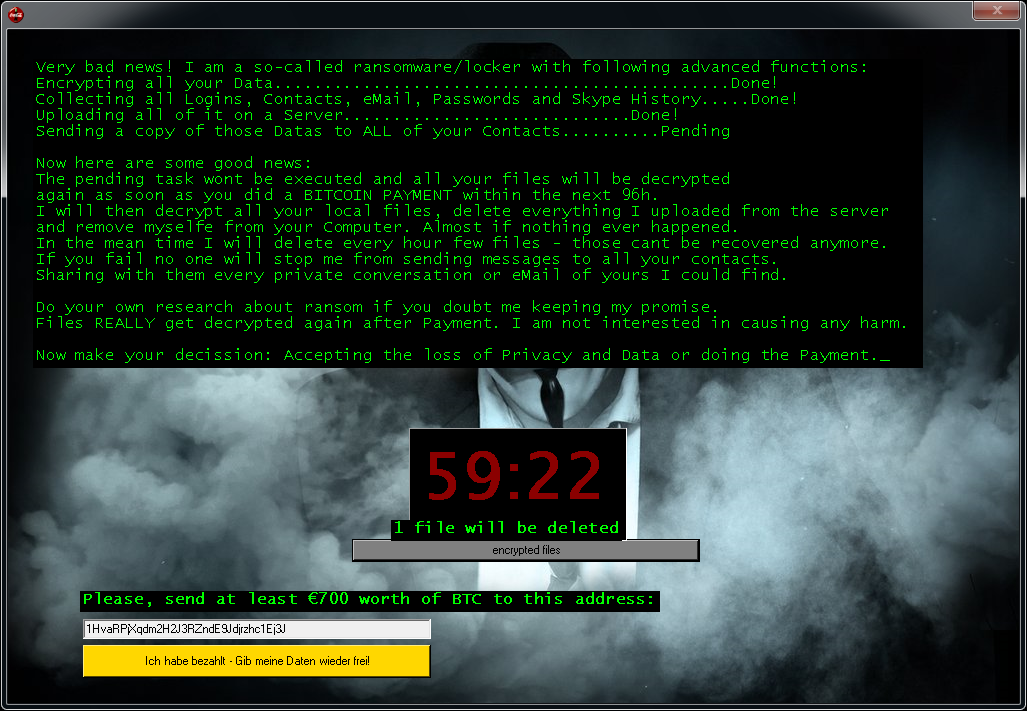
Prometheus
Prometheus ransomware is written in .NET (C#) and encrypts files either using Chacha20 or AES-256. The file encryption key is subsequently encrypted with RSA-2048 and stored to the end of the file. Some variants of the ransomware can be decrypted for free.
Encrypted files can be recognized by one of these file extensions:
- .[cmd_bad@keemail.me].VIPxxx
- .[cmd_bad@keemail.me].crypt
- .[cmd_bad@keemail.me].CRYSTAL
- .[KingKong2@tuta.io].crypt
- .reofgv
- .y9sx7x
- .[black_privat@tuta.io].CRYSTAL
- .BRINKS_PWNED
- .9ten0p
- .uo8bpy
- .iml
- .locked
- .unlock
- .secure[milleni5000@qq.com]
- .secure
- .61gutq
- .hard
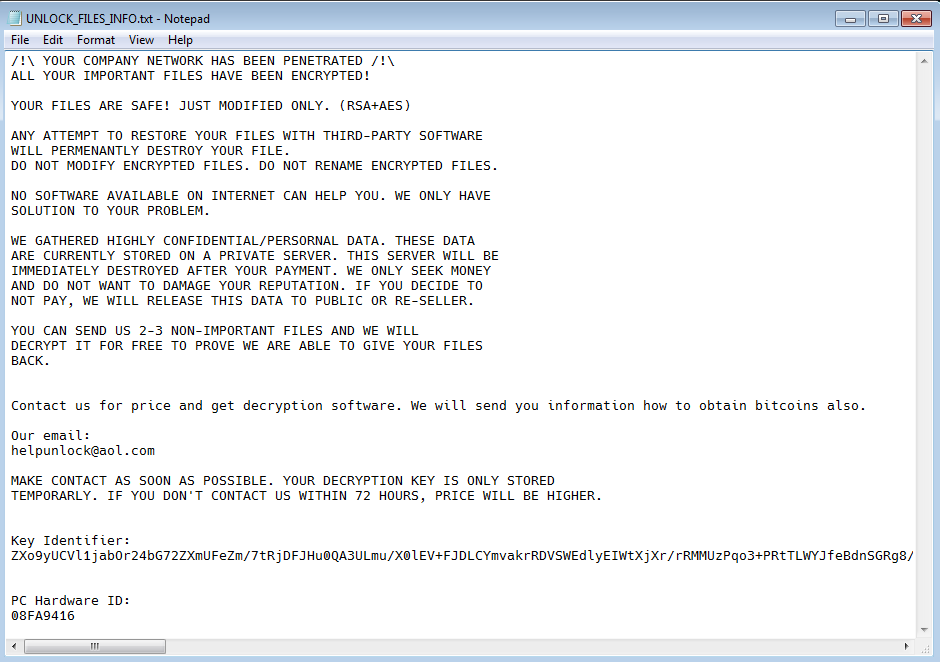
Also, a ransom note file is dropped to the user's desktop with one of these names:
- HOW_TO_DECYPHER_FILES.txt
- UNLOCK_FILES_INFO.txt
- Инструкция.txt
TargetCompany
TargetCompany is a ransomware that encrypts user files with Chacha20 cipher. Victim of this ransomware attack can now decrypt their files for free.
Encrypted files can be recognized by one of these extensions:
.mallox
.exploit
.architek
.brg
.carone
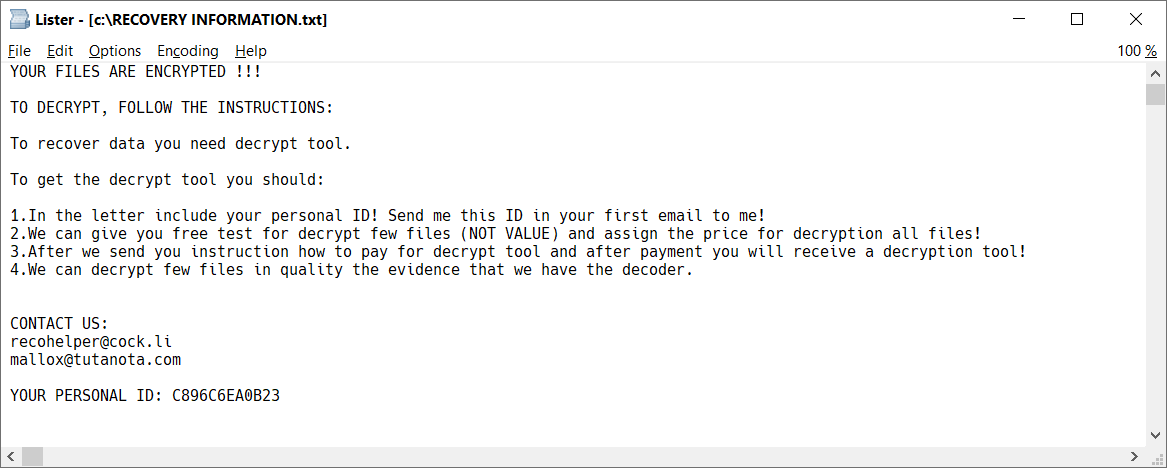
In each folder with at least one encrypted file, there's also ransom note file, named RECOVERY INFORMATION.txt (see the image below).
Stampado
Stampado is a ransomware strain written using the AutoIt script tool. It has been around since August 2016. It is being sold on the dark web, and new variants keep appearing. One of its versions is also called Philadelphia.
Stampado adds the .locked extension to the encrypted files. Some variants also encrypt the filename itself, so the encrypted file name may look either as document.docx.locked or 85451F3CCCE348256B549378804965CD8564065FC3F8.locked.
After encryption is complete, the following screen will appear:
If Stampado has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
SZFLocker
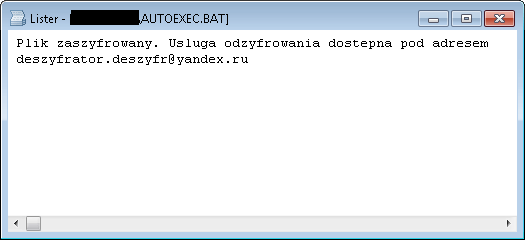
SZFLocker is a form of ransomware first spotted in May 2016. Here are the signs of infection:
SZFLocker adds .szf to the end of filenames. (e.g., Thesis.doc = Thesis.doc.szf)
When you try to open an encrypted file, SZFLocker displays the following message (in Polish):
If SZFLocker has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
TeslaCrypt
TeslaCrypt is a form of ransomware first spotted in February 2015. Here are the signs of infection:
The latest version of TeslaCrypt does not rename your files.
After encrypting your files, TeslaCrypt displays a variant of the following message:
If TeslaCrypt has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
Troldesh / Shade
Troldesh, also known as Shade or Encoder.858 is a ransomware strain that was observed since 2016. At the end of April 2020, the ransomware authors shut their business down and published decryption keys that can be used for decrypting files for free.
More information:https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/shade-ransomware-shuts-down-releases-750k-decryption-keys/
Encrypted files will have one of these extensions:
• xtbl
• ytbl
• breaking_bad
• heisenberg
• better_call_saul
• los_pollos
• da_vinci_code
• magic_software_syndicate
• windows10
• windows8
• no_more_ransom
• tyson
• crypted000007
• crypted000078
• rsa3072
• decrypt_it
• dexter
• miami_california
After encrypting your files, several files are created on the user’s desktop, with name of README1.txt to README10.txt. They are in different languages, containing this text:
The users's desktop background is also changed and looks like picture below:
If Troldesh has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix:
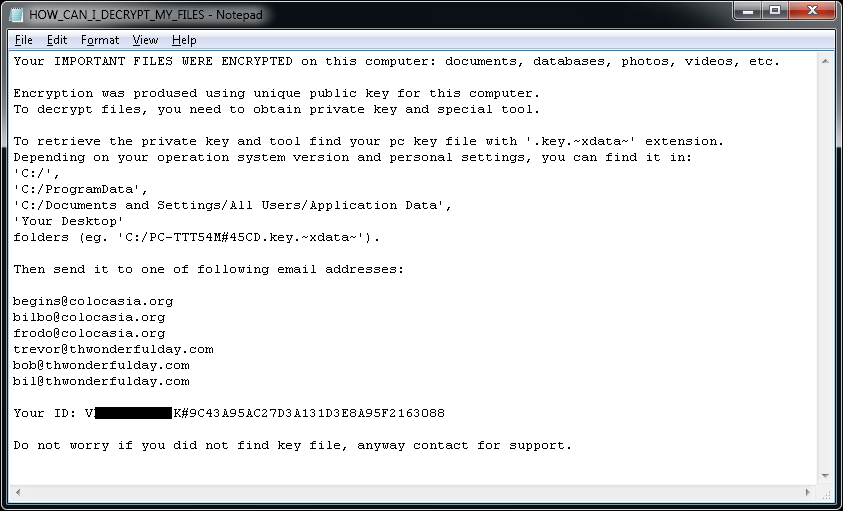
XData
XData is a ransomware strain that was derived from AES_NI and like WannaCry, it uses the Eternal Blue exploit to spread to other machines.
The ransomware adds the ".~xdata~" extension to the encrypted files.
In each folder with at least one encrypted file, the file "HOW_CAN_I_DECRYPT_MY_FILES.txt" can be found. Additionally, the ransomware creates a key file with name similar to:
[PC_NAME]#9C43A95AC27D3A131D3E8A95F2163088-Bravo NEW-20175267812-78.key.~xdata~ in the following folders:
• C:\
• C:\ProgramData
• Desktop
The file “HOW_CAN_I_DECRYPT_MY_FILES.txt” contains the following ransom note:
If Troldesh has encrypted your files, click here to download our free fix: