Common reasons why the internet is not working
There can be a number of reasons for having no internet, even when the Wi-Fi symbol shows that you’re connected. The most common cause is a problem with your router or modem, or a loose cable, but your internet can also fail because of a more technical reason.
Internet connection problems can also be related to internet security — so this is a great time to assess your level of digital protection. Make sure to install the best internet security software once you finish resolving your internet issues.
Here are some of the most common reasons why your Wi-Fi isn't working:
-
Modem or router
-
Your ISP (Internet Service Provider) has an outage
-
Low internet speed
-
Network congestion
-
Physical distance from your router
-
Hacking or network issues
-
Weather conditions
Let’s look at each of these issues so you can figure out why your internet isn’t working properly, locate the cause of your internet problems, and get back online quickly.
 Router or modem
Router or modem
First, check your router and make sure the cables are connected properly and haven’t come loose. Most people have a combined router/modem unit, so you probably have to check only one device. If everything seems fine, a simple reset — or unplugging it and plugging it back in — usually fixes most modem and router problems.
Just like your computer, a modem or router needs to be updated and periodically cleared of temporary files. Updates keep security tight – routers can get malware too – while regular temporary file disposal will reduce the chances of having no Wi-Fi.
You probably don’t think about it, but a router/modem works 24/7, sitting somewhere in your house collecting dust. That’s why a modem/router is the most common reason for the internet not working. Routers and modems can start malfunctioning after just a few years. So, in addition to updating and restarting occasionally, you should also replace your router every five years or so.
 Internet Service Provider outages
Internet Service Provider outages
Your ISP’s connection can go down due to maintenance or mishaps. The best way to check for an ISP outage is by contacting the company. If your ISP is having an outage, wait and the problem will be resolved soon.
Your ISP can also be the cause for slow internet, and they may even decide to slow your internet down on purpose. This is called ISP throttling, and you may want to learn how to get around it.
 Low internet speed
Low internet speed
If your internet is working super slowly, it can prevent you from doing what you need to. A slow internet connection can happen for a number of reasons, and there are many ways to speed up your internet.
For example, your internet speed can slow if you’re uploading or downloading large files. Precious bandwidth is diverted away from your browsing while you upload or download. The same goes for CPU-intensive processes; while these aren’t network problems, they can cause your page-load speed to slow down.
 Bandwidth taken up by multiple users
Bandwidth taken up by multiple users
Speaking of bandwidth, network congestion can slow your internet to a crawl thanks to other members of your household streaming, downloading, gaming, or otherwise consuming lots of bandwidth.
 Physical distance from your router or modem
Physical distance from your router or modem
If your device is too far from your router or modem, your internet speed can also be impacted. So consider moving closer to your router or using a Wi-Fi extender device to improve the range of your connection. Also, try to minimize the number of walls between yourself and the internet device.
 Hacking or network issues
Hacking or network issues
Your internet can stop working thanks to malware or hacking. Hackers have a motive for debilitating your internet, as it makes it more difficult for you to defend yourself. Additionally, some malware is designed to hijack your bandwidth and data — cryptojacking — to mine cryptocurrency.
Network security is more essential than ever these days so always use top quality internet security software. Make sure to learn how to prevent router hacks, too. A non-malicious problem with your network can also leave you with no internet connection, like a DNS cache that needs flushing.
 Weather conditions
Weather conditions
We all know that storms can knock out power lines — but the weather can also affect internet speed even if it doesn’t physically damage any equipment. For example, humidity and rain can interfere with signals.
Weather-related internet problems can come in many different forms. Usually, the only thing to do is wait for the weather to improve and your internet connection to return.
How to fix internet connection issues
There are a number of proactive steps you can take to fix internet connection issues at home. The best place to start is with your router and modem. Unplug your router, wait 10 seconds, and then plug it back in. We’ll look at this in more detail and other top fixes:
-
Restarting your router or modem
-
Checking hardware
-
Checking network settings
-
Advanced troubleshooting
-
Contacting your Internet Service Provider
Restarting your router or modem
When figuring out how to fix no internet connection, restarting your router is the first step. It’s possible your router isn’t connecting to the internet because of a buildup of temporary files, which can cause network connection problems. Restarting your router clears the temporary files from its memory and brings everything back to baseline.
To restart your router or modem, switch it off and keep it unplugged for at least ten seconds so that the device’s memory gets flushed completely. Switch off your computer too. Then, reconnect your router and power your devices up again. Hopefully, this will also fix the Wi-Fi connection on your Android or your iPhone, if that’s also not connecting to Wi-Fi.
Checking hardware
If you have a solid green or white light then your router is working normally. If you see a different light, check your router manual to see what a flashing, yellow, or other light means. Routers and modems are all different, but there is a standard way to tell if they’re working correctly.
Aside from the lights, also check to make sure all cables are fully plugged in and not damaged.
Lastly, try connecting to the internet with another device, like your phone, to determine whether it’s your device or router/modem not connecting to the internet properly. If your phone connects normally, then your internet problem is related to your computer.
Checking network settings
To check the network settings on your device, go to your Wi-Fi network settings, disconnect your Wi-Fi, wait a minute, and then reconnect. Also, try changing the frequency band you’re on by connecting to either the 2.4GHz or 5GHz network (whichever you’re not currently on).
If you’re using a VPN, it might be causing no internet access even though it may appear that you’re connected in your settings. In that case, try disabling the VPN. VPNs are great at keeping a stable connection (and letting you watch streaming services from other countries), but they can run into snags sometimes.
Advanced troubleshooting
Here are some of the more advanced ways you can fix the problem of being connected without internet access:
Diagnose the issue using your computer
On a Windows device, follow these steps:
-
Type network troubleshooting in the taskbar and click Find and fix network problems.
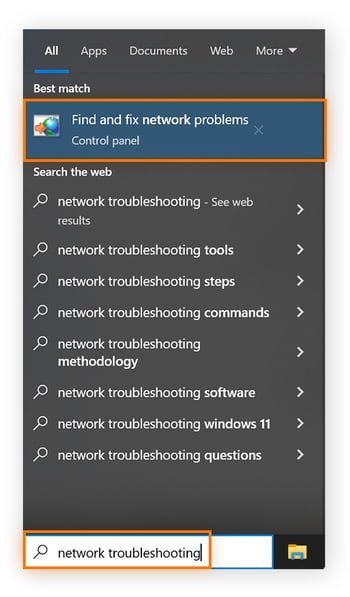
-
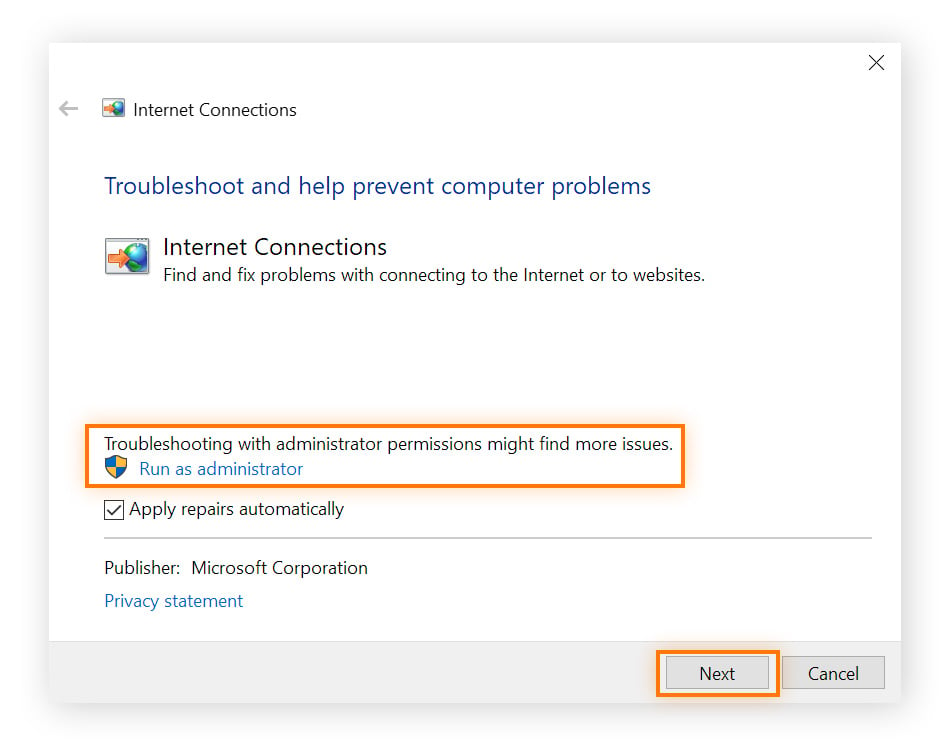
Click Advanced, then Run as Administrator on the new screen before clicking Next. Then choose from the on-screen options.
On a Mac device, follow these steps:
-
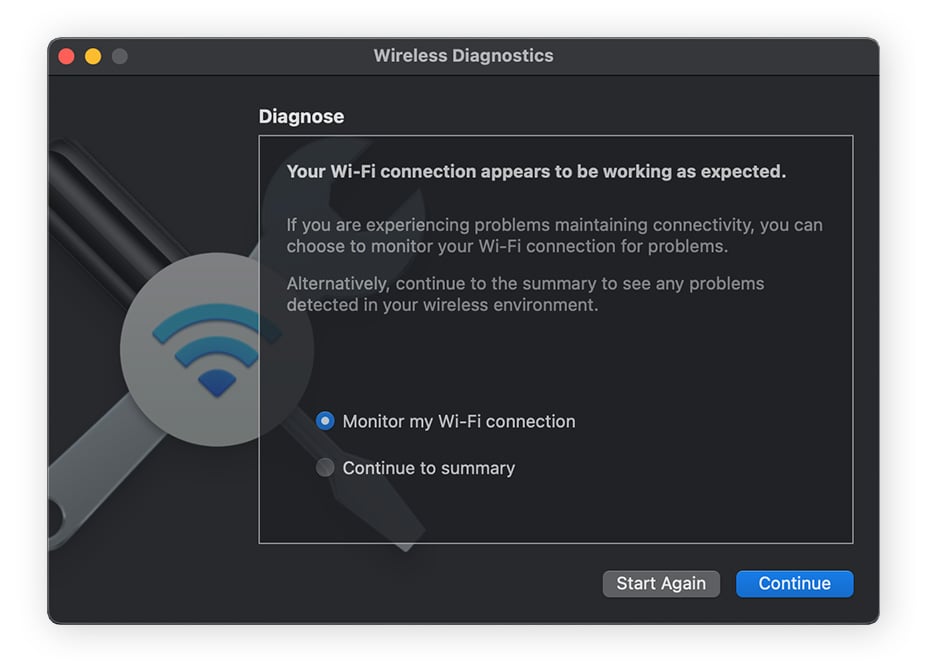
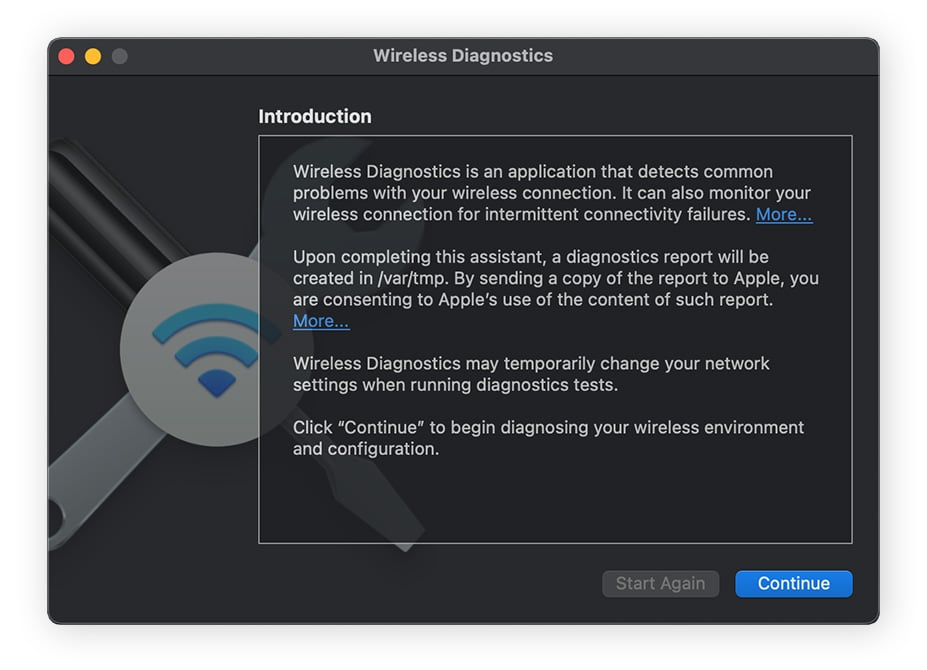
Open a Spotlight search and type in wireless diagnostics. Then open the app and click Continue.
-
When your Mac’s finished running the test, review the results. If there’s an issue found, follow the instructions.
Update your drivers (Windows)
You can also try updating the drivers for your network adapters.
-
Type device manager in the taskbar and click Device Manager.
-
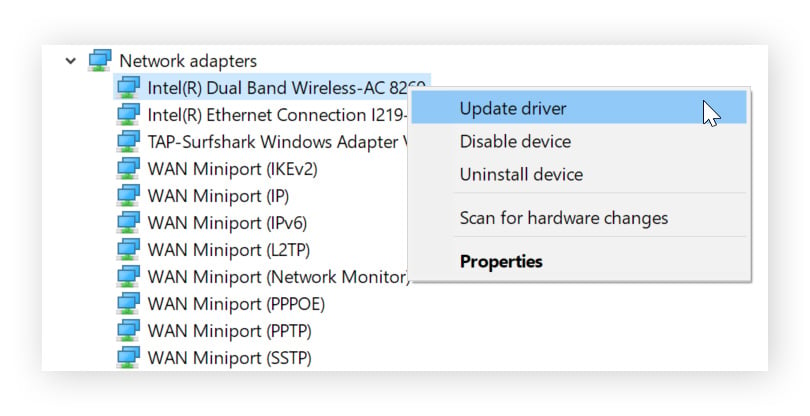
Right-click each of the adapters and click Update driver.
Flush the DNS cache
Now it’s time to try flushing the DNS cache, which holds temporary files that can clog up and slow down your computer.
On Windows:
-
Type cmd in the taskbar and click Command Prompt.
-
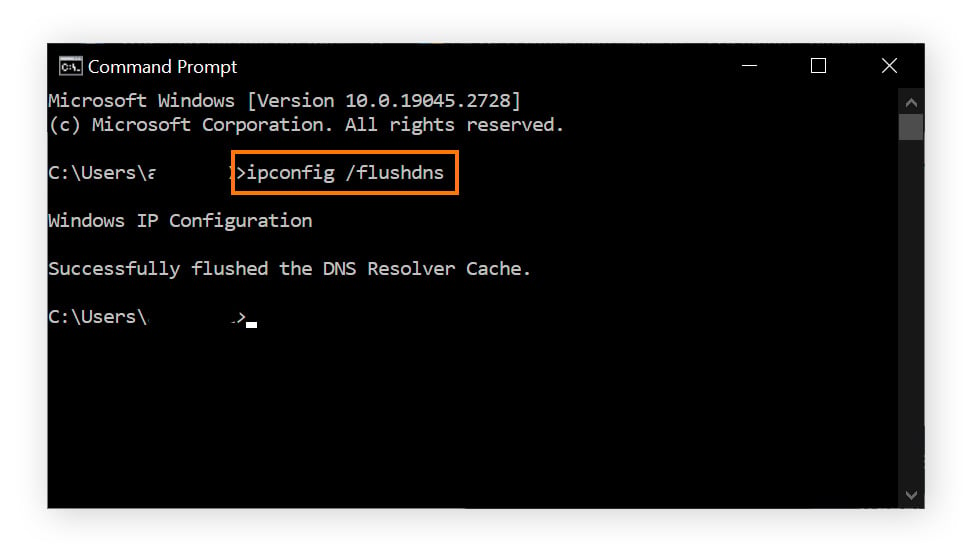
Type ipconfig /flushdns and hit Enter.
On macOS:
-
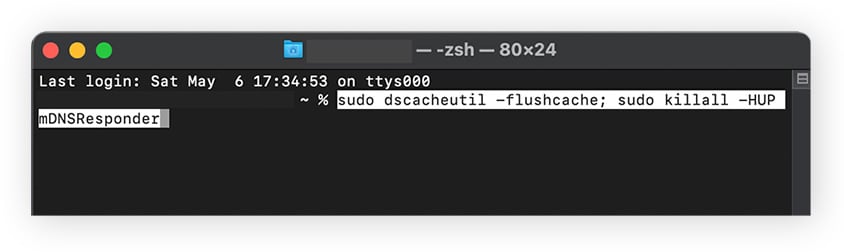
Open a Spotlight search and type terminal, then open the app. Type sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder, then hit Enter.
This works on all later macOS versions from El Capitan up.
-
Type in your password and hit Enter, and your DNS cache will be cleared.
Reset your network settings
If the above fixes don’t work, you can try resetting all network settings. This will revert these back to default settings, which means your Wi-Fi network name and password will be forgotten. Only do this if you’ve tried all other fixes first, and make sure you have all your login details saved somewhere.
On Windows:
-
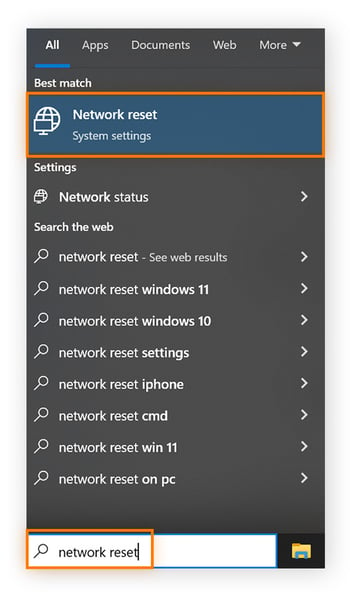
Type network reset in the taskbar and choose Network reset.
-
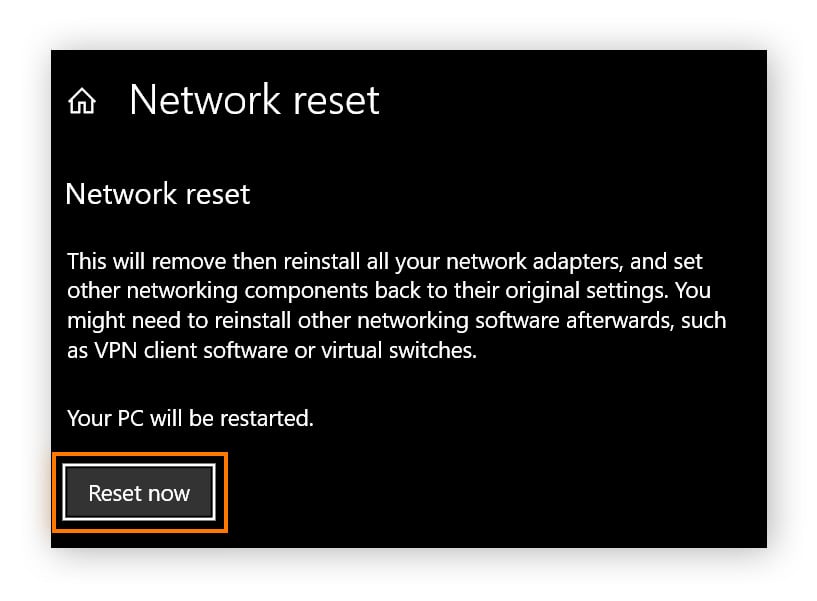
Click Reset now and your computer will restart.
On macOS:
-
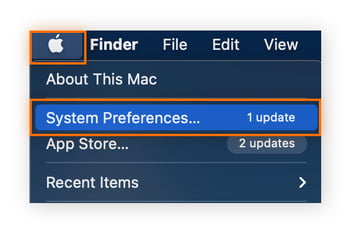
Open the Apple menu, click System Preferences, then select Network on the new screen.
-
Make sure Wi-Fi is selected, then click the - button at the bottom to delete the network.
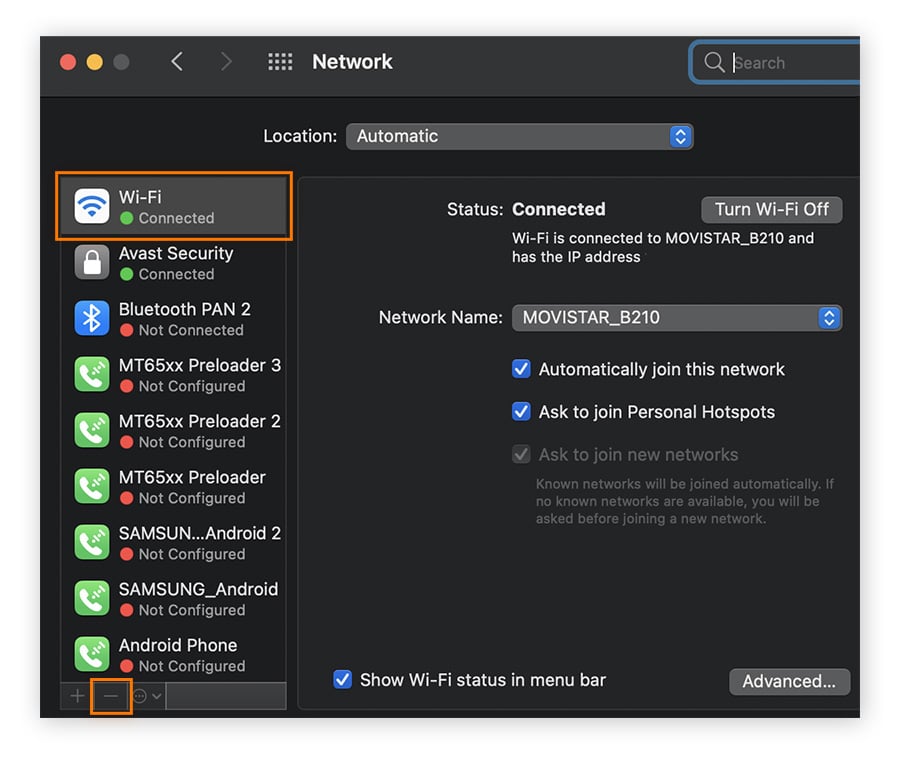
-
Wait for a few seconds, then you can click the + button (next to the - symbol). Click the Interface dropdown list and choose Wi-Fi, then click Create.
Hopefully, this has solved your problem of being connected to Wi-Fi but having no internet. You can also learn how to reset your phone’s network settings and boost your phone’s internet speed.
Contacting your Internet Service Provider
Assuming you’ve tried all the above and your internet still isn’t working, contact your ISP. Ask them, “Why is my Wi-Fi not working?” and be ready to supply information like your account number, email address, and a description of the problem.
They can also walk you through setting a static vs. dynamic IP address.
Secure your Wi-Fi network
Now that you’re back online, make sure you download security software that protects your network and blocks malware that can disrupt your connection. Avast Free Antivirus helps block hackers while keeping you safe from viruses and other malware that can hijack your resources and slow you down. Install Avast today — completely free.
FAQs
How do I fix a Wi-Fi connection that says "connected, no internet"?
Try and fix the Wi-Fi “connected, no internet” message by unplugging your router, waiting a minute, and plugging it back in. Another common solution is to disconnect from (or forget) your Wi-Fi network and then reconnect again. You may also need to update your network drivers.
If neither of these solutions work, you should contact your ISP, who can help you diagnose the cause of the issue — and they may even send you a new router.
What should I do if my Wi-Fi is working but my internet is slow?
Slow internet can be the result of many different causes, like distance from your device to the router, interference from a nearby network, congestion, or old equipment. Try moving closer to your router, connecting to it via an Ethernet cable, or even replacing it.

