What is a QR code?
A QR code (short for Quick Response code) is an array of black and white squares or pixels set in a grid that stores data for a machine to read. A smartphone or camera can quickly process the information contained in a QR code’s specific arrangement of pixels, making it a convenient way to store and access data.
If you’ve used a QR code to access a Wi-Fi network or pull up a menu on your phone, these square codes may seem like modern wizardry, but they were actually invented all the way back in 1994 by the Japanese auto manufacturing company Denso Wave. Initially, QR codes were used to enable high-speed scanning and tracking of components during the assembly process.
Although the QR code meaning has evolved as compatible technology has matured to provide new ways to engage customers, most QR codes (also called qcodes) are designed simply to transmit URLs. As such, using a QR code is like typing a web address into your browser, only faster and more convenient.
If you know how to use QR code, scanning it lets you:
-
View a menu in a restaurant.
-
Get directions to a location in Google Maps.
-
Read more about a product or service.
-
Download an app on the App Store or Google Play.
-
Authenticate an online account.
-
Verify login details.
-
Access Wi-Fi by storing SSID, password, and encryption type.
-
Send and receive payment information.
How do QR codes work?
QR codes work by arranging a series of black and white pixels into a unique pattern that encodes a string of data. When scanned, the pattern of the qcode can be translated into human-readable information.
If you know how to scan a barcode using a laser-reader, you already know how to scan a QR code — the only real difference is the type of device used to read the code. But unlike barcodes’ linear arrangement, QR codes can store much more data, because they’re written both vertically and horizontally.
All QR codes have a standard structure that makes information readable. Let’s break it down:
-
Quiet Zone: The empty white border around the outside of a QR code.
-
Hinder pattern: The three black squares in the bottom-left, top-left, and top-right corners.
-
Alignment pattern: A small square near the bottom-right corner, which ensures the QR code can be read, even if it’s skewed or at an angle.
-
Timing pattern: An L-shaped line that helps to identify individual squares within the whole code, making it possible for a damaged QR code to be read.
-
Version information: Identifies which version of the QR code is being read.
-
Data cells: The rest of the QR code communicates the actual information — the URL, phone number, or other data.
Usually, you don’t need to use a special QR app scanner — smartphones will link to the content in the QR code when you point your camera app at it. If you’re offline or think you’ll need to access the code again, taking a picture of it will make the QR code scan again when you view it later.
How to scan a QR code with an iPhone or iPad
Scanning a QR code on an iOS device is easy, because the QR reader in iPhones and iPads is fully integrated with the Camera app. Simply view the QR code through the camera and the QR code scanner will take care of the rest.
Here’s how to scan a QR code on an iOS device:
-
Open the Camera app by swiping up from the bottom of the screen and tapping the camera icon.
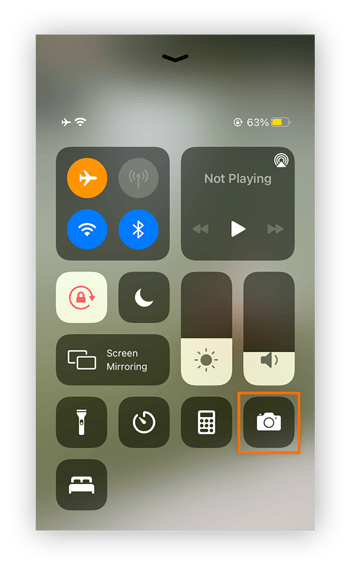
-
Hold the phone so the entire QR code is visible in the frame (you don’t need to take a picture).
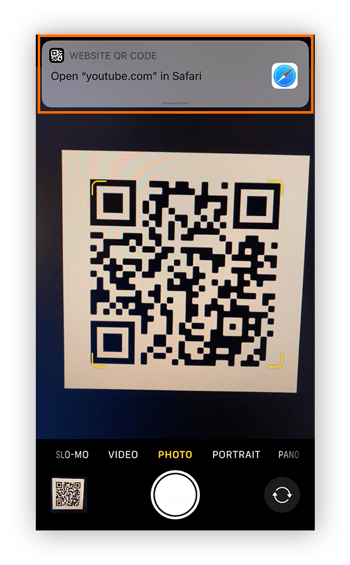
-
Once the QR code has been read, a notification will appear at the top of your screen. Tap it to follow the link contained in the code.
Remember that you won’t be able to access the link if you aren’t online. BUt you can take a picture of the QR code to rescan it again later.
If no notification comes up, check to make sure you have the Scan QR code feature enabled in your Camera app. This is usually turned on by default, but it may have been switched off accidentally.
How to enable or disable the QR code scanner in iOS
Here’s how to enable or disable the QR code scanner on an iPhone or iPad:
-
Go to Settings and scroll down to Camera.
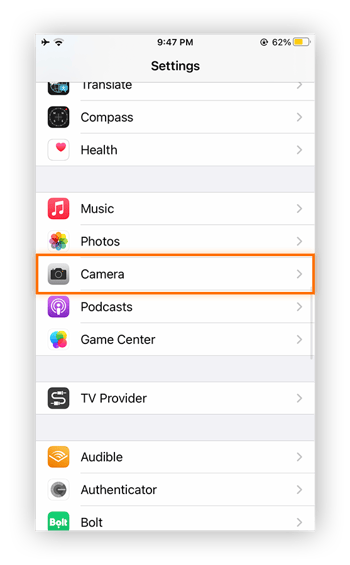
-
Tap the toggle next to Scan QR codes so that it’s enabled (green). To disable the QR code scanning feature, turn this toggle off.
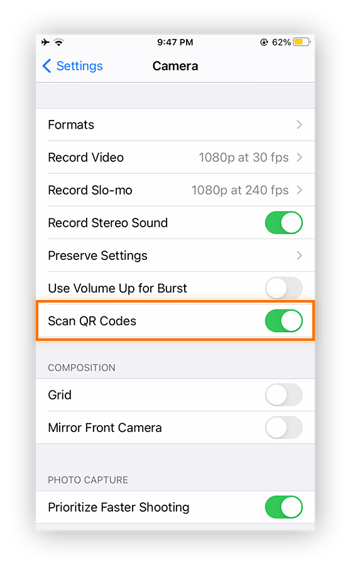
Your QR code scanner is now enabled, and your camera app will automatically scan codes until you choose to disable the function.
How to scan a QR code on an Android phone or tablet
Scanning a QR code on an Android phone is easy, and Android’s QR code scanner is automatically enabled.
Here’s how to use the QR code scanner on an Android phone or tablet.
-
Open the camera app on your Android.
-
Hold the device so the whole QR code is present in the frame (you don’t have to take a picture).
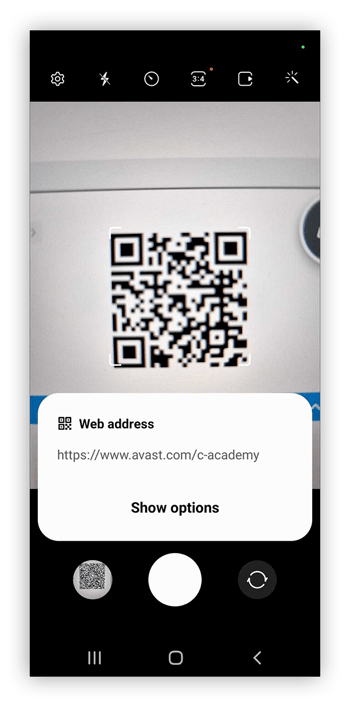
-
Then, tap the decoded link that appears on your screen.
Google Lens
Google Lens is designed to provide information on whatever you point your camera at, and it can handle a QR scan quite easily. Google Lens is available as a standalone app or through the Google app itself.
Here’s how to use the Google QR scanner with Google Lens:
-
Open the Google app and tap the Google Lens camera icon next to the microphone icon in the search bar.
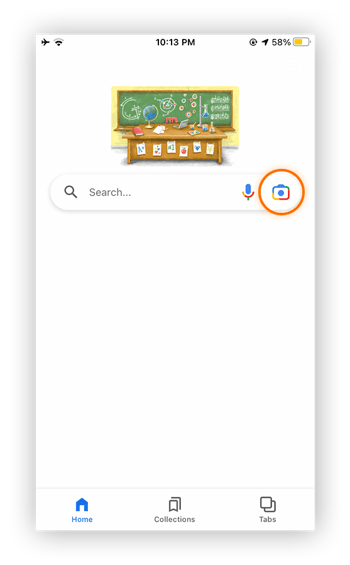
-
Allow Google to use the camera by tapping Open camera (or tap Search with your camera).
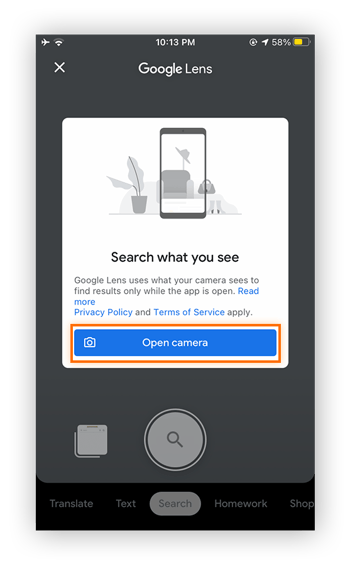
-
You should see a camera view in the app now. Hold the phone so that the whole QR code appears in the frame and tap the notification that appears at the top.
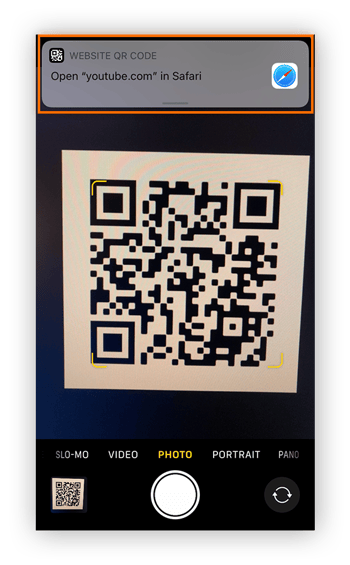
If everything works correctly, you’ll be linked directly to the content, whether it’s a restaurant menu, promotional offer, or a link to a video.
How to scan a QR code on a PC
If you don’t have access to a smartphone, you can read QR codes from your PC using either a webcam or by opening an image file with the code in it.
Here’s how to scan a QR code using your Windows computer.
-
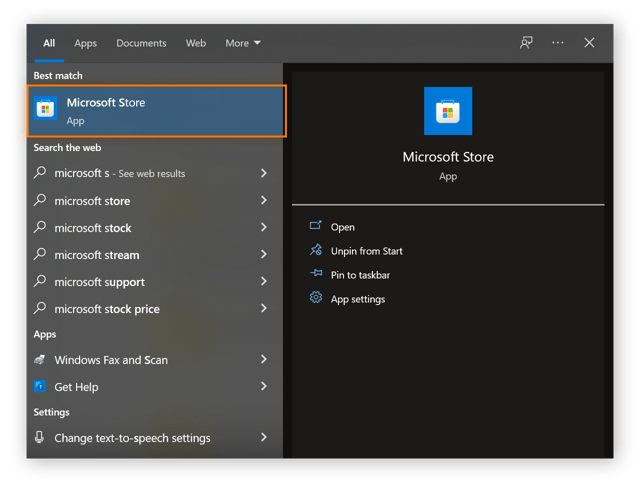
In the Start menu search bar, type Microsoft store and click the search result to launch the app.
-
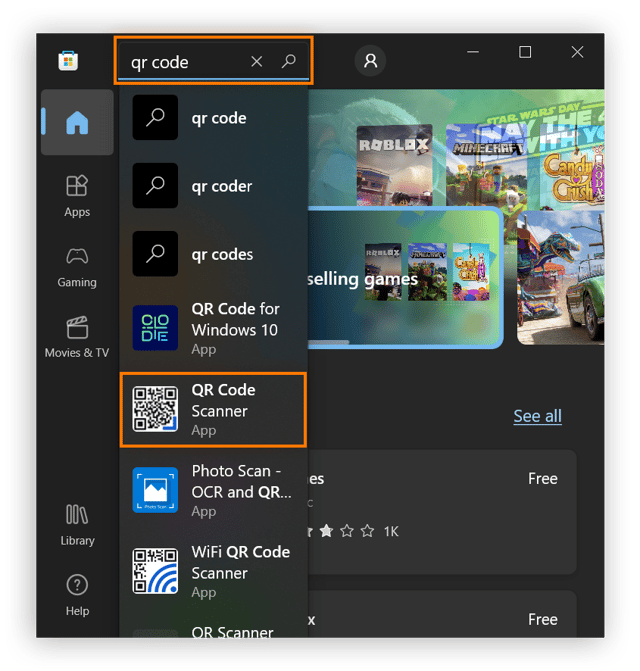
Search for “qr code scanner” in the Microsoft Store and click QR Code Scanner in the search results.
-
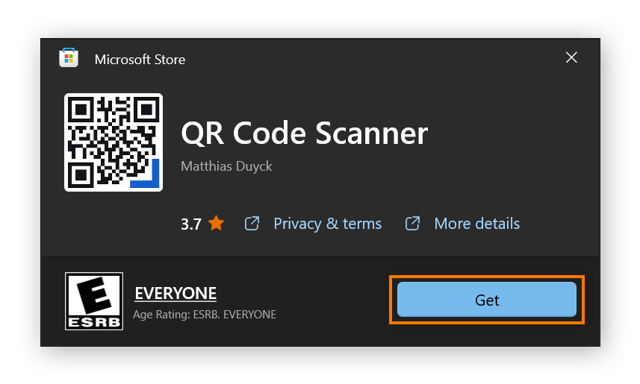
Click Get to download the scan code reader, then click Open.
-
When the app asks for access to the camera, click Yes. You can now scan codes by holding the QR code up to the webcam.
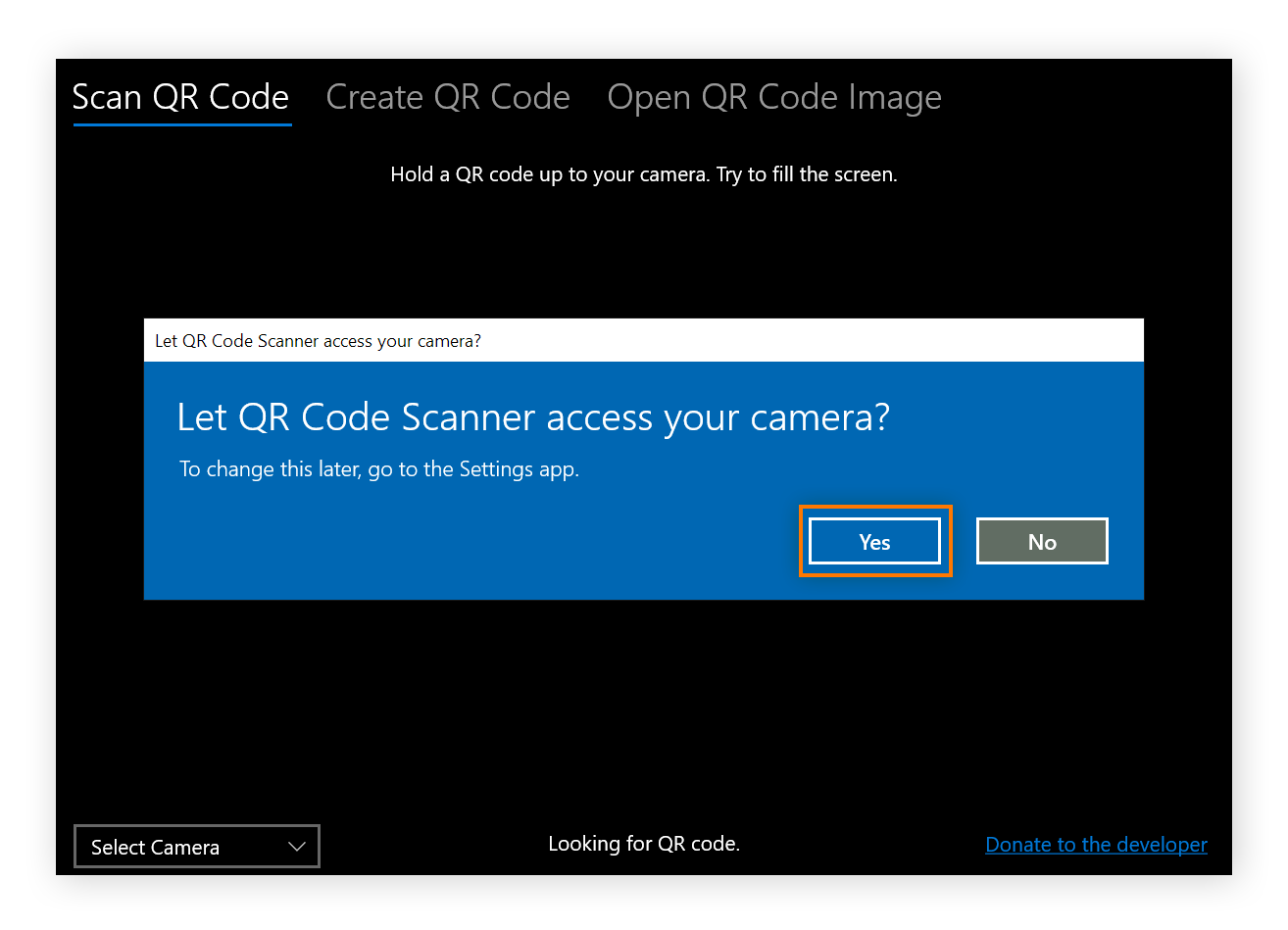
If you don’t have a webcam, you can use the app to read a QR code from an image on your computer by clicking Open QR Code Image.
How to scan a QR code on a Mac
You can also scan a QR barcode with a Mac, but you need to install a third-party app. Here’s what you need to do:
-
Download a QR scanning app from the App Store (here we’re using QR Journal).
-
Open the app and hold up the QR code so that it’s fully visible in the frame.
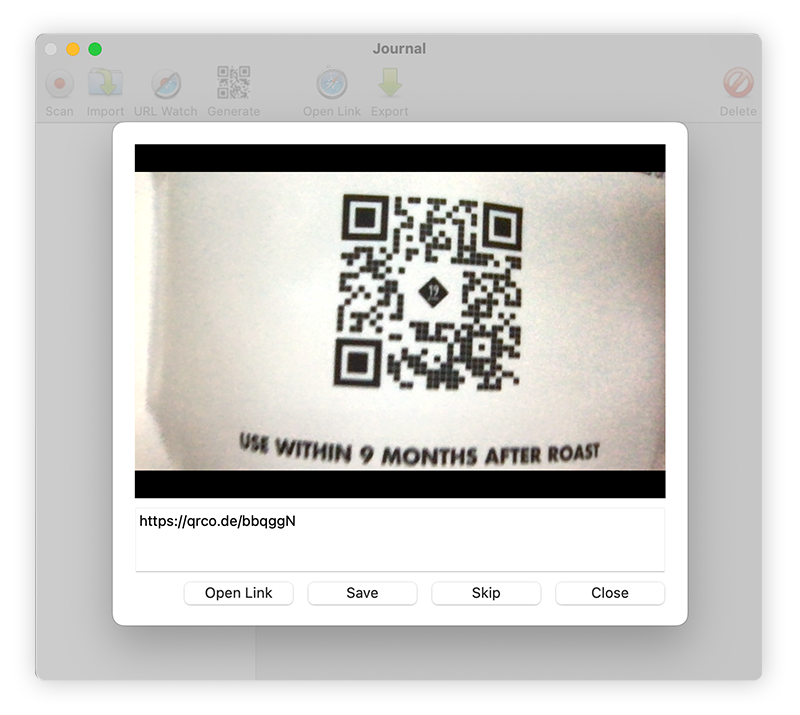
-
The QR code reader will detect the data and share the link with you automatically. If you’re connected to the internet, you can open the link immediately. Or, you can save the encoded link to check it out later.
Now that you know how to visit a website with a QR code on your Mac, make sure to review your Mac security to help defend against malware and phishing threats.
Types of QR codes
Aside from each QR code being entirely unique, there are several different types of QR codes. Some contain only black and white squares, while others have particular symbols in the center. While all QR codes perform the same basic function, some differ in how they read and write information.
Here are some different types of QR codes for links, tracking data, and other info:
-
QR code: The original version of the QR code created by Denso Wave in the 1990s.
-
Aztec code: Contains concentric squares in the center and doesn’t require a “quiet zone” around the edge.
-
Maxi code: Used by the US postal service.
-
PDF417: A mix between a QR code and a barcode.
-
Semacode: Has no need for the components of a QR code, like the hinder pattern.
Each of these QR formats has different pros and cons, like varying levels of readability when part of the encoded image is damaged, or different amounts of data that can be stored in a given amount of space.
A QR code’s data capacity is determined by storage type, or “mode.” Here are the various storage modes a QR code app can read:
-
Numeric mode: A string of numbers.
-
Alphanumeric mode: A string of numbers and letters.
-
Byte mode: 8-bit single-byte code.
-
Kanji mode: Japanese characters.
QR code examples
There are all sorts of uses for QR codes beyond accessing restaurant menus and validating concert tickets. For example, by making information more readily accessible, QR codes can help improve education practices and enable more integrated healthcare systems.
-
Product packaging: These QR codes can reveal nutritional information or special offers.
-
Customer support: Quickly scanning QR codes can help customers access customer support more quickly.
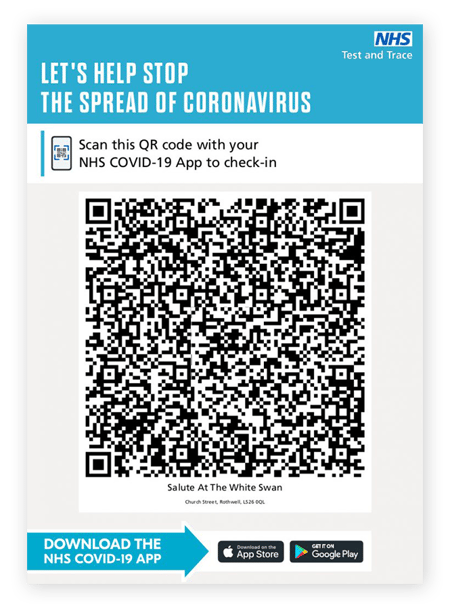
-
Coronavirus tracing: In the UK, as in many other countries, visitors to hospitality venues are invited to scan a QR code upon arrival using a Covid-19 track and trace app.
-
Postal services: QR codes can help you or your postal service track packages and other shipments.
-
Education: Schools use QR codes to help engage with students and locate resources.
-
Social media: People can easily share social media profiles and specific content via 24fps QR codes.
Third-party apps
Using third-party scanning apps for mobile isn't recommended. Most smartphones already come with fully integrated, safe and effective QR scanning technology, and using untrusted apps may compromise your privacy and security. It’s also needlessly complicated — why not just open the camera, point, and scan?
Are QR codes safe?
QR codes are generally very safe. While they record the scanning location, time, and operating system used, they don’t collect any personal information and cannot be hacked. But QR codes are only as safe as the links they contain, and while mobile devices can’t generally get viruses, QR codes can be used as a backdoor for other mobile threats.
Hackers can use malicious, spoofed QR codes to link people to dangerous websites containing phishing scams or drive-by malware that doesn’t require any user interaction to infect your device. If you do fall prey to a dodgy QR code, knowing the signs a phone has been hacked can help you take swift action to prevent the exploit developing into a more serious threat.
QR code scams
A common QR code scam involves printing flyers for fake services and including dangerous QR codes on them. In 2020, parking meters in Austin, Texas bore stickers offering online payment for parking, but the QR code led to a fake website that took payments and stole credit card information. Not only were victims duped out of their money and sensitive financial information, but they were fined for parking illegally.
While the vast majority of QR codes are perfectly safe, you shouldn’t trust every QR code you see. Be careful of codes posted publicly or sent to you via email, and always look at the link’s URL before clicking it. Just like any other link or site, if something doesn’t feel right, go elsewhere.
Safeguard your devices with Avast
As QR codes become increasingly ubiquitous, the risk of encountering a malicious QR code, or clicking on other dodgy links, increases — and mobile devices are particularly vulnerable. That’s why you need comprehensive cybersecurity software protecting your devices.
Avast Free Antivirus is packed with layers of protection, providing real-time security against malware, phishing, and fake websites. Download Avast for free today and turn your phone or computer into a fortress.

