What is Tor Browser?
Tor (The Onion Router) is a web browser that lets users access a network that anonymizes web traffic to provide private web browsing. Often used to access the dark web, Tor Browser hides IP addresses and browsing activity by redirecting web traffic through a series of different routers called nodes. Because Tor hides browsing activity and blocks tracking, it’s used by whistleblowers, journalists, and others who want to protect their privacy online.
Tor anonymizes web traffic with a special encryption technique originally developed by the US Navy to help protect American intelligence communications. Today, Tor is an open-source, privacy platform available to anyone, although the Tor Blog has mentioned countries where its use may be blocked.
Besides working as a web browser, Tor also provides onion services via its onion network to enable anonymity for websites and servers. A [dot]onion web address, which is exclusively accessible via Tor Browser, protects the identity of both websites and visitors through complex, encrypted, and anonymous connections. As such, Tor is the very definition of a dark web browser.
Keep reading to learn how Tor works. And before you dive in, we’ll explain how to use Tor to access the dark web.
How does Tor Browser work?
Tor uses onion routing to encrypt and reroute web traffic through Tor’s onion network. After your data is secured inside multiple layers of encryption, your web traffic is transmitted through a series of network nodes, called onion routers. Each router (or node) then “peels away” a layer of encryption until the data reaches its final destination, fully decrypted.
When you make a request, the packets (blocks of data) in the request are encrypted individually. Tor then transmits the multi-layered encrypted data across three layers of international proxies that make up the Tor circuit, which decrypt one layer each. Let’s take a closer look at the three layers of network nodes:
-
Entry/Guard node: First, Tor Browser randomly connects to a publicly known entry node. The entry node introduces your data into the Tor circuit by decrypting the first layer of encryption to uncover the address of the middle node, where it forwards your data.
-
Middle node: This node receives the request from the entry node. It knows the IP address of the entry node where the request came from, but it doesn’t know the encrypted IP of the original requester. The middle node decrypts the next packet, revealing the next node in the circuit, but the content and final destination of the request remain encrypted.
-
Exit node: The exit node receives the request and decrypts the last packet, revealing the final destination. Once the last layer of encryption is peeled off, the decrypted data leaves the Tor network and reaches its final server destination.
 Tor Browser sends web traffic through an entry node (blue), middle node (green), and exit node (orange) to encrypt and decrypt traffic.
Tor Browser sends web traffic through an entry node (blue), middle node (green), and exit node (orange) to encrypt and decrypt traffic.
Simply put, onion routing is how Tor works, and how dark web websites can be browsed without anyone except you knowing. Sounds complicated, right? That’s because it is. But fortunately, knowing how to use Tor Browser doesn’t require a PhD in computer science — it’s surprisingly easy and user-friendly.
Does Tor Browser hide your IP and how?
Yes, Tor hides your IP, concealing it and making it difficult for anyone to trace your internet activity back to you. In addition to relaying your data through network nodes to hide your location and identity, Tor’s onion routing uses multi-layered encryption to provide even more robust privacy protection.
Because Tor-encrypted data is sent through randomized nodes in a network of over 7,000 nodes (relays) before it’s fully decrypted, by the time internet traffic reaches its destination, its origin is obscured. This elaborate process shows how secure Tor is at protecting data and hiding your IP address from websites, your ISP, and even the government.
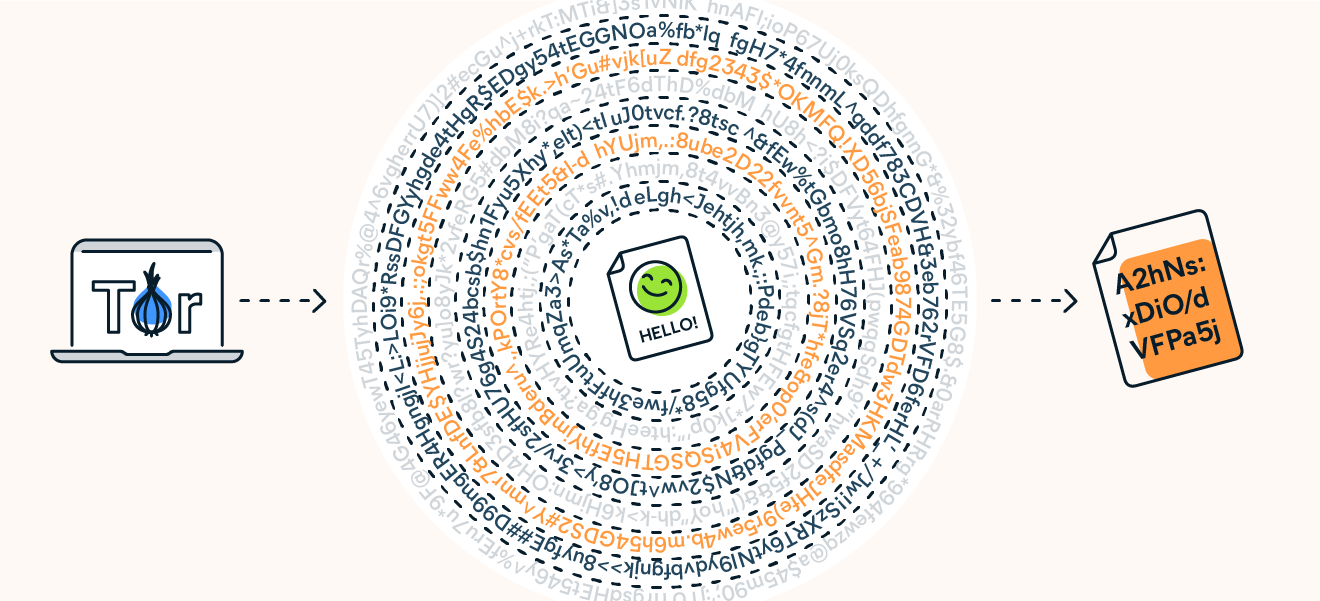 Your web traffic goes through thousands of layers of decryption when connecting to the internet via Tor Browser.
Your web traffic goes through thousands of layers of decryption when connecting to the internet via Tor Browser.
Is Tor Browser anonymous?
Tor Browser is anonymous in terms of hiding your location and browsing activity — but there are limits. Although they can’t see your browsing activity or Tor-encrypted data, your ISP can still see that you’re using Tor. You can also be identified if you log into an online account or provide personal details to a website while using Tor.
What is the difference between Tor Browser and a proxy server?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between you and host services, while Tor is an encrypted network of decentralized servers. While proxies replace your IP address and location, they don't encrypt internet traffic, meaning your data is still exposed in transit. Tor Browser both anonymizes and encrypts your location through onion routing, better protecting your data when you get on the dark web.
Using a proxy server in combination with Tor Browser can help to hide the fact that you’ve connected to the dark web, but it won’t confer any additional cybersecurity benefits. Not sure which private browsing tool you need? Read our guide to see whether a VPN, proxy, or Tor is best for you.
Is Tor a VPN?
Tor is not the same as a VPN, though both tools provide encryption and reroute your web traffic to another network. A key difference between Tor and a VPN is that a VPN’s network is operated by a central service provider, while the Tor network is decentralized and run by volunteers. Tor is specifically designed to be a dark web browser.
In addition, Tor and VPNs take different approaches to rerouting data. A VPN sends your web traffic to a server, which transmits it to the internet. Tor’s onion routing method reroutes your data through a series of independent nodes. Though Tor is slower, the process of rerouting data through nodes makes it more difficult to trace your activity back to you.
What is Tor Browser used for?
Tor Browser is primarily used as a method of anonymous browsing. From journalists and civil society organizations to regular individuals with online privacy concerns, Tor Browser users are a diverse group. But criminals also take advantage of Tor’s anonymity to carry out illegal activities both on and off the dark web.
Here are some activities the Tor Onion Browser is used for:
-
Practicing freedom of speech: Journalists often use Tor to stay safe and report freely. It helps them protect sources, reach users worldwide, and publish sensitive stories without risking retaliation. Citizens in countries where internet access is censored may also use Tor to access restricted content and exchange information.
-
Illegal activities: Cybercriminals can use Tor to stay hidden on the dark web. Dark web markets offer pirated media, hacking services, illegal drugs, compromised data, and other illicit goods and services. Tor originally gained notoriety from its use by the now-defunct, international dark web marketplace Silk Road.
-
Whistleblowing: Whistleblowers often use Tor because it helps them protect their identities while exposing sensitive information. Open-source whistleblowing framework GlobaLeaks recommends using Tor to protect users’ anonymity.
Can I be tracked while using Tor?
Despite its impressive privacy features, there are still ways that you can be tracked while using Tor on the dark web. Onion routing is a sophisticated means of preventing location tracking, but there's no such thing as complete online anonymity.
Although your internet traffic is encrypted and routed through multiple layers on Tor, your ISP can still see that you’re connected to Tor. Plus, Tor cannot protect against tracking at the entry and exit nodes of its network. Anyone who owns and operates the entry node will see your real IP address. And at the exit node, your decrypted traffic is vulnerable to interception.
You can reinforce Tor’s weak spots by pairing it with a VPN that provides end-to-end encryption. That means your web traffic will be encrypted at the entry and exit nodes of the Tor network, and using VPN-over-Tor will keep your real IP address safe from anyone lurking at those gateways.
 Use Tor alongside a VPN to ensure your web traffic is fully encrypted.
Use Tor alongside a VPN to ensure your web traffic is fully encrypted.
Advantages of using Tor Browser?
One of the main advantages of using Tor browser is the high level of privacy provided by the onion network. Not only do Tor’s security protocols allow users to access sites safely and hide their IP address, but the browser is open source, free, and simple to use, especially considering the complex protection it provides.
Here are some of the advantages of using Tor:
-
No tracking cookies: By default, Tor does not store cookies, and clears your browsing history, cookies, and cached web content when you exit the browser. Cookies are a common means of web tracking used by advertising agencies, e-commerce sites, analytics companies, and tech giants. Tor lets you browse without leaving a trail.
-
Enhanced privacy: The onion browser method was designed to keep online data, location, and browsing history private. Whether you want to look at sites without worrying who’s watching, have health concerns you want to keep to yourself, or just want to feel more secure online, Tor offers peace of mind.
-
Safer browsing on public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi can be a sketchy place to transmit data. Hackers can set up fake networks or packet sniffers to steal your data, and anyone with the know-how can intercept your transmissions in what are known as man-in-the-middle-attacks. But you should still always connect to a VPN before using any browser, including Tor, on public Wi-Fi.
-
Combatting censorship: Many countries censor journalists and citizens, and bar access to social media sites such as Facebook or Reddit, as well as well-known news organizations. Accessing Tor helps people access websites that may be restricted in the countries they’re in. Companies such as Facebook, the BBC, and The New York Times have their websites available as a Tor Onion Service.
Disadvantages of using Tor Browser
Although Tor is a sophisticated privacy tool, it has several disadvantages — some of which counteract its cybersecurity advantages.
Here are the disadvantages of using Tor:
-
Slow Speeds: Tor is a slow browser. Onion routing encrypts web traffic and sends it through a series of network nodes. That’s great for privacy, but the elaborate process results in slow speeds compared to other browsers. Although there are ways of making Tor faster, you can’t significantly boost speeds.
-
Stigma: Tor has acquired the unfortunate stigma of dark web illegality. ISPs and governments may take note of people who use the browser. For people seeking privacy, Tor may bring them the opposite.
-
Blocking: Some network administrators block Tor. Some websites also keep track of and block web traffic coming from Tor exit nodes. But you can mask node usage by using Tor bridges or a VPN.
-
Vulnerabilities: Though Tor is designed for anonymity, the onion network is vulnerable at the entry and exit nodes. Since internet traffic is not encrypted at these points, your data is liable to interception, and your IP address could be exposed.
Is Tor illegal?
Tor is not illegal in the US. Tor is often associated with dark web criminality, but the dark web also hosts many legitimate resources like the dark web wikipedia, secure email services, and research databases. If you’re not engaged in illicit activities, it’s not a crime to use the dark web to protect your privacy.
Still, Tor and the dark web have a stigma attached due to the undercurrent of illegal activities. Using Tor can call undue attention to your web activity, which is counter-productive if you’re seeking privacy. ISPs have been known to throttle internet speeds and even contact customers about Tor usage. Your government may also track your activities if you use Tor.
Some countries, such as Russia, have been working to ban Tor. If you’re interested in anonymous browsing, first check whether Tor, or even VPNs, are legal in your country.
Is Tor Browser safe?
Tor Browser is generally considered safe and secure thanks to the onion routing protocol that encrypts your data and hides your IP address. But Tor does have some vulnerabilities, and as with any browser, Tor users remain vulnerable to online threats, ranging from malware to phishing scams.
Knowing how to safely use Tor means using it alongside other cybersecurity tools, so set up a VPN to benefit from end-to-end encryption. And make sure your network’s protected by a firewall and the best antivirus software.
How to stay safe while using Tor Browser
Along with setting up a VPN, firewall, and antivirus, there are some other measures you can take to use Tor safely:
Boost your security levels
Tor Browser has three security settings: Standard, Safer, and Safest. Standard allows full access to all websites as they are. Safer disables website features that often cause security issues, but this also causes some sites to lose functionality. Safest only allows features needed for basic services and static sites, and this also limits functionality on some sites.
Here’s how to change Tor’s security to the safest setting:
-
In the top-right corner, click the shield icon, then Settings.

-
Tor will scroll to the Security Level section automatically, where you can choose Safest.

Only use HTTPS sites
The “S” in HTTPS stands for secure, and signifies that a website has an SSL Certificate and encrypts data traveling between your device and a website. As Tor is encrypted by default, most dark web websites don’t use this same certification. But, while you’re on the surface web, stick to HTTPS sites for the best security.
Never reveal personal information
Keep your personal details to yourself, including your name, address, phone number, email, and social media profiles. The purpose of Tor is to remain anonymous, and entering any personal information online could comprise it. Plus, it’s rarely necessary to share these details on the dark web.
Only download files from trusted sources
The dark web is full of cybercriminals who know curious users are checking out Tor. Some scammers prepare fake downloads infected with viruses and other malware. Only click links and download files from trusted sources.
Download antivirus software
Make sure you have a reputable antivirus running on all your devices. Use security software like Avast One to help protect against online threats.
Tor Browser and the dark web
For many, Tor is synonymous with the dark web — the unindexed part of the internet that’s only accessible with certain browsers. The connection between Tor and the dark web started with the Silk Road dark web market, where customers could buy drugs and other illegal goods. When in operation, the notorious online marketplace could only be accessed through Tor.
As a browser that enables anonymity to both website hosts and visitors, the appeal of Tor to dark web participants is obvious. And though the dark web is not just a haven for illicit activity, accessing the dark web via the onion browser is popular with criminals. That’s why dark web scans are important so you know if your personal information is compromised.
But the Tor network was not designed with criminality in mind, nor was it intended to be the “dark web browser.” Tor is a legitimate and effective online privacy tool and can also be your browser of choice on the surface web. The Tor routing innovations created for US intelligence agents are now used by a variety of everyday users who value their online privacy and data security.
Other dark web browsers
Though Tor Browser has strong ties with dark web browsing, it also has competition. There are other browsers that can also access the dark web. Though Tor enables anonymity, these other browsers have their own pros and cons.
Here are some other dark web browsers:
-
I2P - Invisible Internet Project: Similar to Tor, this is a fully-encrypted, private network layer. In I2P, every user acts as a node, instead of having volunteer-run nodes like Tor.
-
Subgraph OS: While not a browser itself, this open-source operating system is designed to be resistant to surveillance and snoops. It incorporates Tor into its ecosystem.
-
Hyphanet: Hyphanet, formerly known as Freenet, is a peer-to-peer platform for publishing and communication that is censorship-resistant and respects privacy. It’s available for Windows, macOS, GNU/Linux, and POSIX systems.
-
Firefox: Though this popular and accessible browser can access the dark web if you know how to configure the proxy access, it lacks some of Tor’s safety features for the dark web.
-
Waterfox: Based on Firefox, the Waterfox browser is fast and features tracking protection to safeguard your privacy.
The default Tor search engine is a dark version of DuckDuckGo, but there are other dark web search engines you can use on Tor.
How to use Tor Browser
Tor Browser is currently available for Windows, Mac, Linux, and Android — you can download it from the official Tor website. After installation, you can use Tor to access the public internet as well as .onion websites.
Here’s how to download and install Tor Browser on Windows, Mac, Linux, or Android:
On Windows PC
-
On the Tor project website, go to the Tor Browser download page. Click the Windows icon.

-
Once downloaded, choose where you want to install Tor and install it.

-
Launch Tor Browser from your download location and click Connect.

On Mac
-
Go to the Tor Browser download page. Click the Apple icon.

-
Drag the Tor Browser icon over the Applications icon.

-
Launch the Tor Browser application and click Connect.

On Android
Download Tor Browser from the Tor Project website or open the Google Play Store, search for Tor Browser, and tap Install. After installation, you can open Tor directly or launch it from your home screen.

After you get Tor set up on your device, you may want to change your default browser for maximum privacy. Check out our review of the best browsers for security and privacy.
Can I get Tor Browser on iPhone?
You can’t get Tor Browser for an iPhone. iOS requires browsers to use Webkit, which Tor Browser doesn’t allow due to privacy concerns. Tor recommends iOS alternatives, Onion Browser or Orbot, for open-source browsers that use similar technology to Tor.
How to uninstall Tor Browser
Here’s how to uninstall Tor Browser on Windows:
Here’s how to uninstall Tor Browser on Mac:
And here’s how to uninstall Tor Browser on Android:
Browse securely and privately online
Though Tor is a powerful tool for anonymous browsing on the dark web, it’s not without flaws. Tor is slow, and it may attract unwanted attention from your government or ISP. If you’re looking for a safe, secure, and private alternative for surfing on the surface web, get Avast Secure Browser.
Light, fast, and easy to use, Avast Secure Browser is designed by security experts to boost your online privacy. It will help stop hackers from stealing your data, block malicious links, force websites to use encryption, and warn you about dangerous websites you may be about to visit. Download Avast Secure Browser today for better security, control, and performance.