Defragmentation is a key factor in PC performance. In simple terms, defragmentation — or defragging — is the process of re-arranging files on a hard disk for faster access. In this article, we provide step-by-step instructions on how to defrag your computer hard drive.
Before getting started, consider using an automated tool like Avast Cleanup, which defrags your hard drive, puts performance-sapping apps to sleep, and clears out unwanted files. And if you’re a Mac user, check out our guide to defragging a Mac.
How to defrag Windows 10 and Windows 8 PCs
Defragging your hard disk on Windows 10 and Windows 8 is straightforward, and it helps get the files on your hard drive in order. Here’s how to defrag a computer:
-
Click the Start button in the bottom-left corner of your screen and type the word defrag.
-
Then select Defragment and Optimize Drives from the list of options.
-
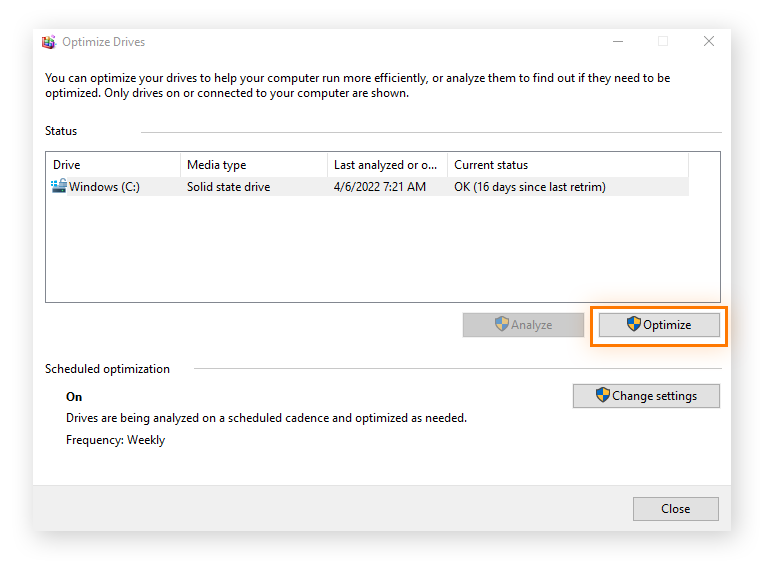
Click Optimize. This analyzes the disk’s fragmentation level and launches the defragmentation process. This can take a few hours to finish. While in process, don’t do much work on your PC, aside from maybe some light browsing.
-
When the defragmentation process is done, you’ll see OK in the Current status column, as shown above.
How to defrag Windows 7 PCs
Here’s how to defrag your computer’s disk drive if you’re running Windows 7:
-
Click the Start orb in the bottom-left corner and type defrag.
-
Then select Disk Defragmenter from the search results.
-
Click Defragment disk to launch the defragmentation process.
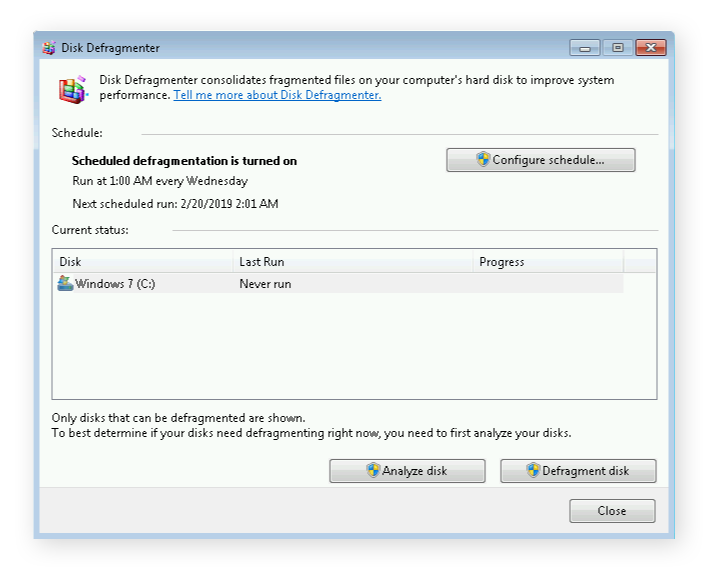
If you have a lot of files on your system, or if your computer hasn’t been defragged in a while, this could take up to a few hours. Let it run and don’t interfere with it — leave your PC alone.
Use a third-party defrag utility
Using third-party utilities and PC optimizer tools makes defragmentation — and PC cleaning overall — a lot easier by automatically handling routine maintenance. These tools diagnose issues and prescribe fixes, saving you from having to deal with defragmentation and other time-consuming cleanup processes yourself.
Avast Cleanup is packed with features for speeding up your computer and fixing annoying problems. With Avast Cleanup’s dedicated defrag program, you can service your hard drive at the click of a button, or even set the defragmentation process to run regularly and automatically, so you don’t have to think about defragmentation ever again.
What is disk defragmentation?
Defragmentation organizes storage on your computer by consolidating files and other data saved on your hard drive. When there’s not enough space on your disk to store an entire file in one place, the file is broken down into smaller pieces called fragments. Defragmentation puts those pieces back together.
What does defragging your computer do?
Defragmentation reverses the process your computer uses to break up data when it saves files to your hard drive. Defragging reformats your drive, reconstituting the files that were fragmented when they were written (saved) to your disk.
To understand how defragmentation affects your PC’s performance, let’s look at the anatomy of a traditional hard disk. A hard drive is made out of mechanical components, with multiple discs stacked on top of one another and rotated through a spindle. These discs — also called platters — contain data. To retrieve data, your computer accesses the discs using the read/write heads (similar to your grandparents’ vinyl record player).
Over time, the amount of fragmented data spread over a hard drive’s mechanical components can grow alarmingly high. Defragmentation puts those separated pieces of data back together again. The result is that files are stored in a continuous manner, which makes it faster for your computer to read the disk and retrieve the files you need, increasing the overall performance of your PC.
Figuring out how to defrag a computer seems like an unnecessary task these days. “Defrag your disk” sounds like ancient advice, a recommendation you’d get back when it was common to run Windows 98 on an old Pentium II computer. Back then, “Defrag!” was regular advice when your system slowed to a crawl. But even though people don’t talk about it anymore, defragmentation is still necessary for ideal performance, and it can save you from having to wipe an old hard drive simply out of sheer frustration.
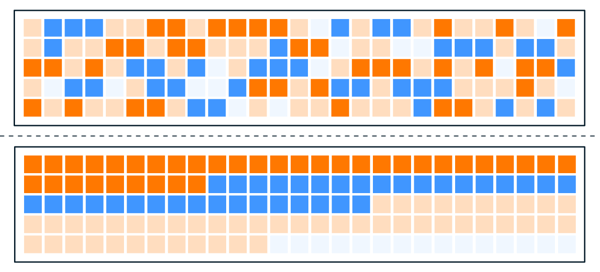 Defragmentation takes the scattered data in your hard drive (above) and organizes it (below) for more efficient retrieval.
Defragmentation takes the scattered data in your hard drive (above) and organizes it (below) for more efficient retrieval.
The difference between SSDs and HDDs
Hard disk access is a highly mechanical process, even though so many other computer components are purely digital. And disk access is the slowest part of computing. It can typically take 5-15 milliseconds for your computer to access the bits and bytes on a traditional hard disk drive (HDD), whereas accessing data on a modern solid state disk (SSD) or in RAM is done in a fraction of a millisecond.
Aside from the time it takes to access files, the overall throughput of hard disks is also low. Typical HDD speeds are 100 MB/sec for larger files and 0.5-1 MB for small file fragments (which are more common in day-to-day operations). Check out our detailed guide to learn more about the differences between SSDs and HDDs.
But the key takeaway is that old-school HDDs are extremely slow. So slow, in fact, that the rest of your system has to wait a while for the hard disk to read data. It’s especially noticeable when you start Windows, launch programs, or open big files. That’s why operations can feel very slow on PCs with a hard disk (which are still fairly common).
A fragmentation primer
In theory, any file on your hard disk could be stored in a continuous manner on a platter. Perhaps, when your computer is brand new, saving files starts out that way. But as you move, delete, and copy files regularly — and uninstall programs — file sizes grow. Then, with all the additional data, your entire file no longer fits in the original space it was allocated to. The result is gaps, empty spaces on your hard disk, because your files need to be broken up in order for all the data to be saved.
Imagine you clean up your computer by deleting five GB of data from your hard disk, leaving a five-GB gap in the middle of space otherwise occupied by Windows, your applications, and data files. The next day, you download the next hot game, which may be about 20 GB. Your hard disk stores the first five GB of the game in that gap you recently freed up, and it breaks up the remaining 15 GBs into fragments and stores them into other free spaces or slots them at the end of the occupied disk space.
Now your new game is split up, or fragmented, into two or more pieces. The read/write head of your mechanical hard disk now has to piece together the files for the game when you launch it. Stitching those files together takes more time than it otherwise would if the data were kept in one continuous block of information.
That’s an oversimplified example. On a freshly formatted hard drive and cleanly installed Windows PC, the fragmentation level is near zero. But in reality, your computer winds up with loads of free spaces. The operating system splits up data and programs into so many pieces it makes your head spin, so you should test your hard drive regularly to make sure it’s still healthy.
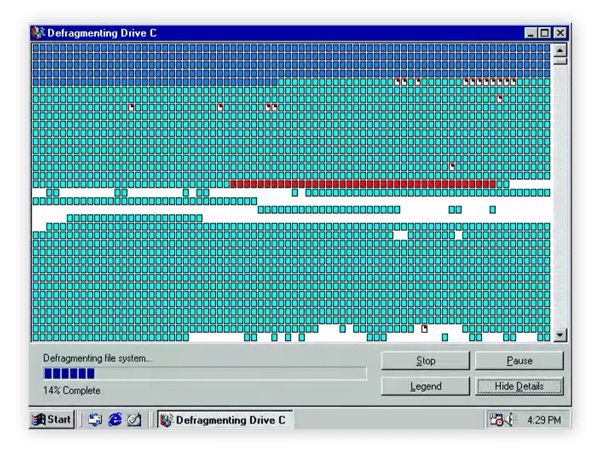 DOS or Windows 95 used to show the gaps on your hard disk and how it was being put together. These old DOS and early Windows utilities no longer exist, but the concept and process remains.
DOS or Windows 95 used to show the gaps on your hard disk and how it was being put together. These old DOS and early Windows utilities no longer exist, but the concept and process remains.
How often should you defrag your computer and when?
Most Windows versions (like Windows 7 and Windows 10) defrag the disk automatically on a regular basis. But if you’re constantly working on your machine, Windows never gets around to this background task. That’s why knowing how to defrag a computer is helpful — you can run the defragmentation process yourself (see steps above) and check on the fragmentation status.
On one of my computers, the automatic defragmentation process hadn’t run for 12 days and was 25% fragmented. That had a negative effect on performance, and defragging resulted in immediate and noticeable benefits.
Other ways to speed up your computer and boost performance include using a registry cleaning tool or pausing background processes to reduce PC fan noise.
Is it safe to defrag? Can I defrag an SSD?
Defragging a traditional hard disk drive is safe and easy, and it keeps your disk healthy. Regular defragmentation and other maintenance tasks help your computer run smoothly, and the risk of damage to your hardware or files is extremely small, even if the process is disrupted mid-flow.
But there’s no need to defrag an SSD. And don’t worry if you’re not sure whether you have an SSD or an HDD. When you launch the defragmentation process, Windows will tell you whether it’s looking at a hard disk or an SSD. If you have an SSD, the Optimize button on the defrag screen will perform a so-called TRIM operation instead of a standard defragmentation.
TRIM tells the SSD which data blocks are no longer needed and can be reused (after you’ve deleted a file, for example). The next time an application writes data to storage, a data block doesn’t need to be erased first to create room. That’s one way that SSDs improve performance and reduce wear and tear.
Maintain computer performance after defragging
Defragmentation is a great place to start, but it’s just one part of good Windows hygiene. To more completely clean up and optimize your computer, get a software tool to take care of the work for you. Avast Cleanup is a light and powerfully effective tool that will streamline your computer automatically. Clear out gigabytes of unnecessary files, remove bloatware, and get automatic maintenance to keep your PC running smoothly.