What graphics card do I have?
Here’s how to find out info on what graphics card you have:
-
In the desktop search bar, start typing Device Manager and select it when the option appears.
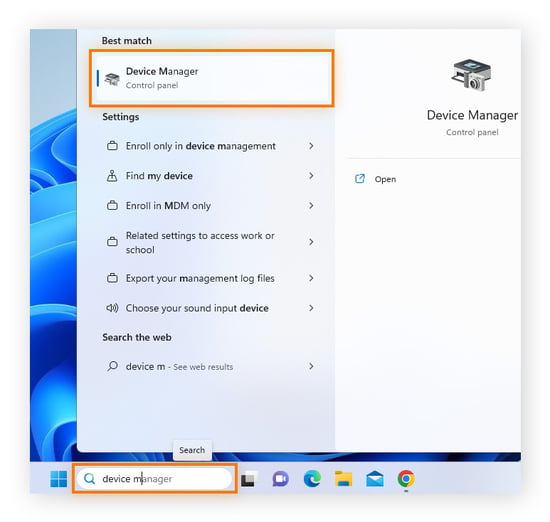
-
Click the arrow next to Display adapters and the name and model of your GPU will appear right below.
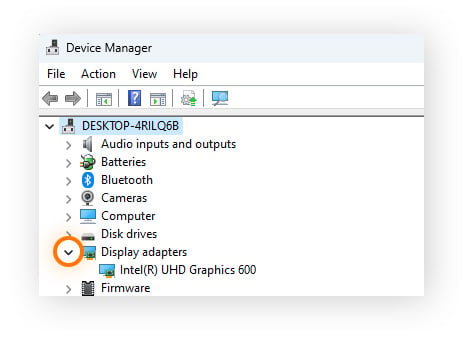
If you double-click the name of the card, you can view device properties, inspect the details of your driver, and identify any driver updates available.

Note: You can use these steps to check a graphics card on a Windows 11, 10, 8, and 7 device.
External GPU cards
If you use one, here’s how to find out what external GPU (eGPU) you have:
-
In the desktop search bar, start typing Device Manager and select it when the option appears.
-
Click Display adapters near the top of the list of entries. Then, click the drop-down arrow and look for the name and model of your eGPU — it will be separate from your computer’s built-in GPU.
An external GPU or external video card is a quick way to improve the graphics capabilities and gaming experience on an aging laptop — like ones with VGA ports. Just be sure to assess your hardware, and do some research before deciding on one — in some cases, you may be better off upgrading your laptop entirely.
Learning what graphics card you have is a start, but learning how to check your PC graphics card in a laptop or desktop will help you understand its exact specs and get the most out of it for graphics-intensive tasks.
5 ways to check your GPU on Windows
Ensuring you’ve got the right graphics specs is critical, especially when it comes to gaming, HD video editing, and running other graphics-intensive applications. Are you wondering: What GPU do I have? Thankfully, there are a number of easy ways to detect graphics hardware on Windows.
Windows System Settings
System Settings let you check your graphics card status and inspect its range of properties and compatibilities. In Windows, video card status and other information relating to your display can easily be found in the Settings app. You can also update Windows drivers or update audio drivers through a similar process.
Here’s how to check your GPU through Windows 11 System Settings:
-
Open Settings through the Start menu and click System, then Display.
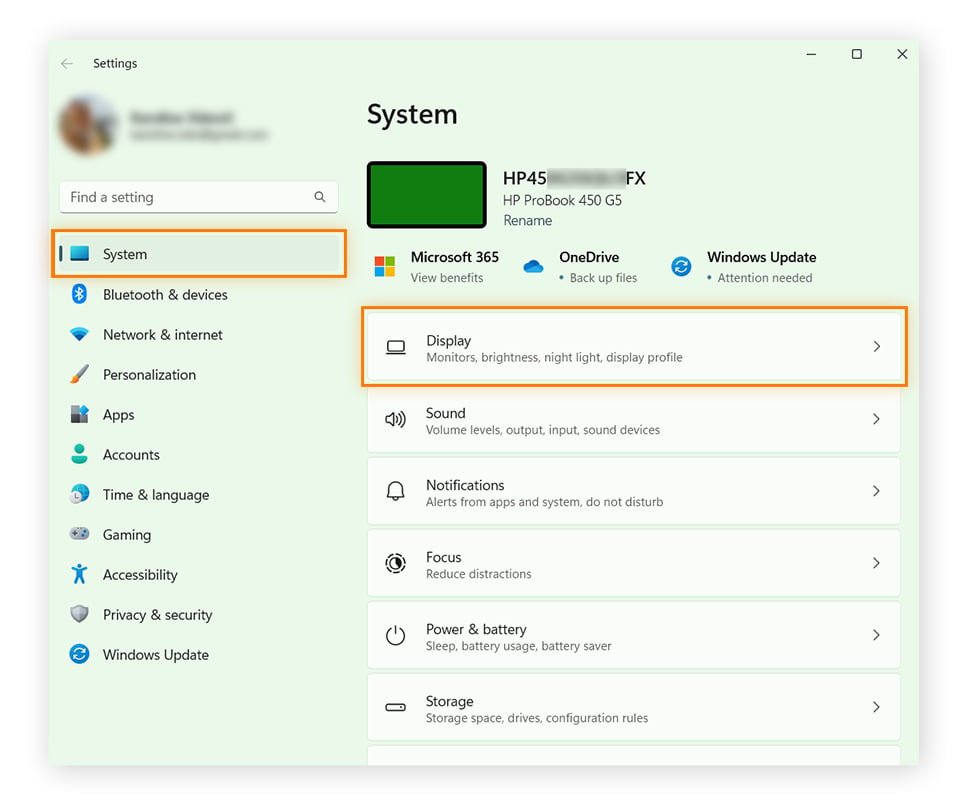
-
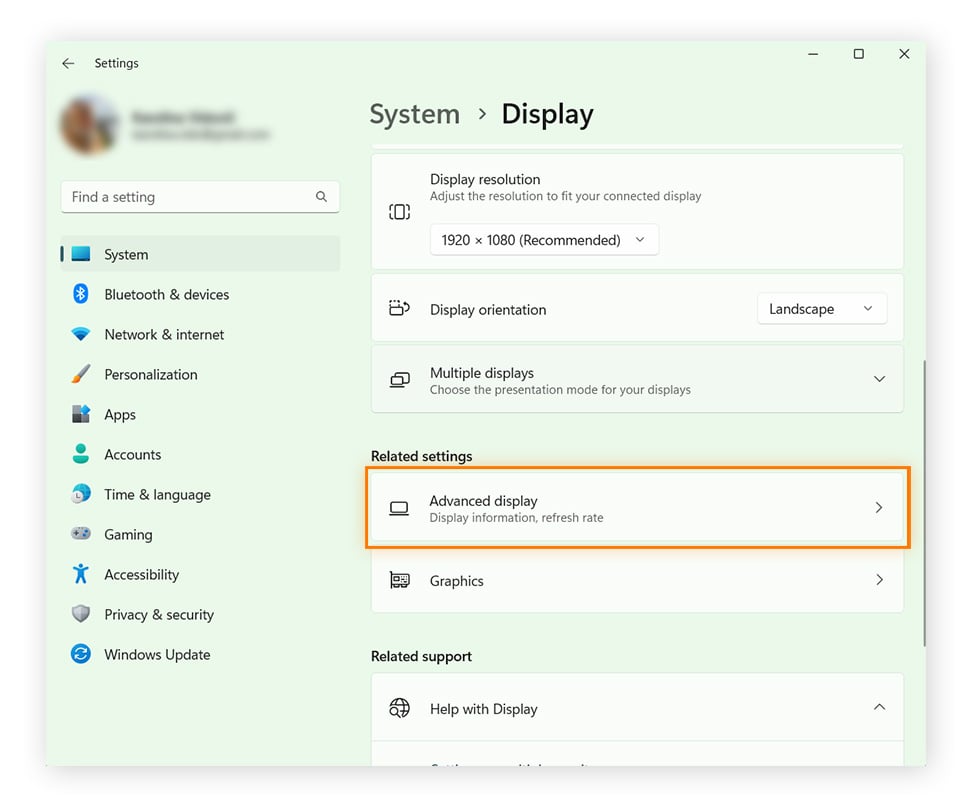
Scroll down to “Related settings” and click Advanced display.
-
Under Display information you can see which graphics card is installed on your PC as well as other important metrics impacting your computer graphics, like your desktop resolution and refresh rate.
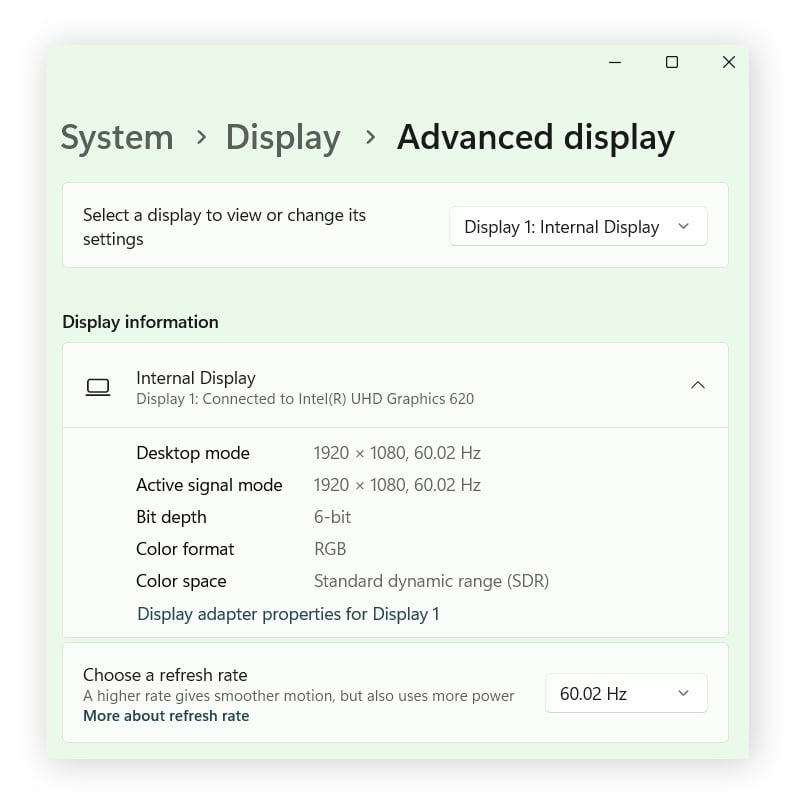
To complete this same process in Windows 10, click Start > Settings > System > Display > Advanced display settings > Display information.
System Information
The System Information app is a great tool for looking under the hood of your machine to examine your graphics card and accompanying drivers. It’s also a great tool to check your RAM.
Here’s how to check what GPU you have through System Information:
-
Open the Start menu or go to the desktop search bar, start typing system information, and select it when the option appears.
-
Click the + symbol next to Components in the upper left, and then click Display on the expanded list.
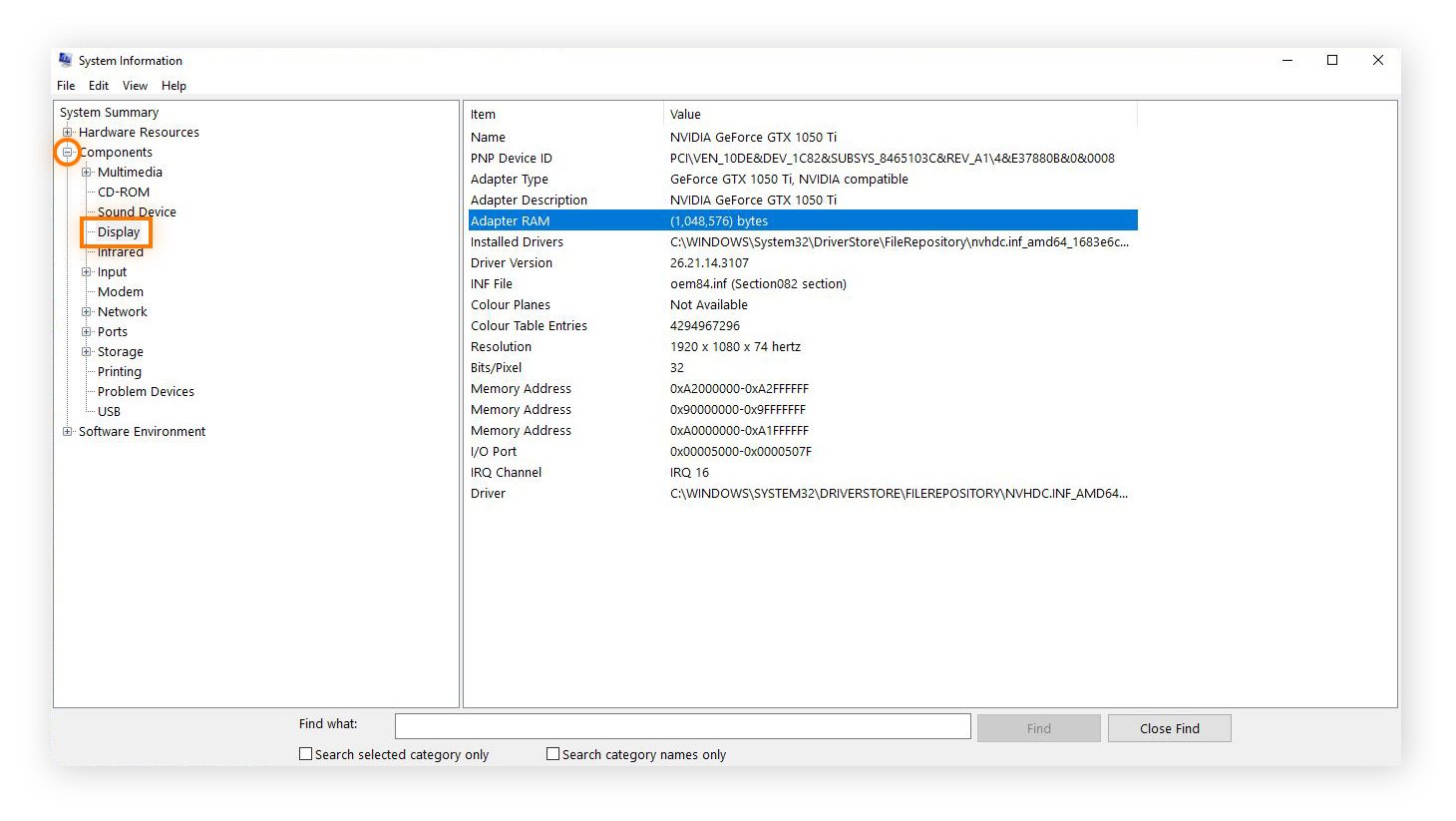
You’ll see the name of your graphics card, its type, and device ID. You’ll also see details about your driver installation and how much RAM your GPU has to call upon.
Windows Task Manager
While a graphics card refers to the graphics hardware extension as a whole, the graphics processing unit (GPU) is the specific component that actually processes graphics. You can use Windows Task Manager to check your GPU chip in detail. Here’s how:
-
Open the Start menu or the desktop search bar, start typing task manager, and select it when the option appears. You can also press Ctrl + Alt + Del on your keyboard and click Task Manager on the list that appears.
-
On the Task Manager window, click Performance and select GPU.
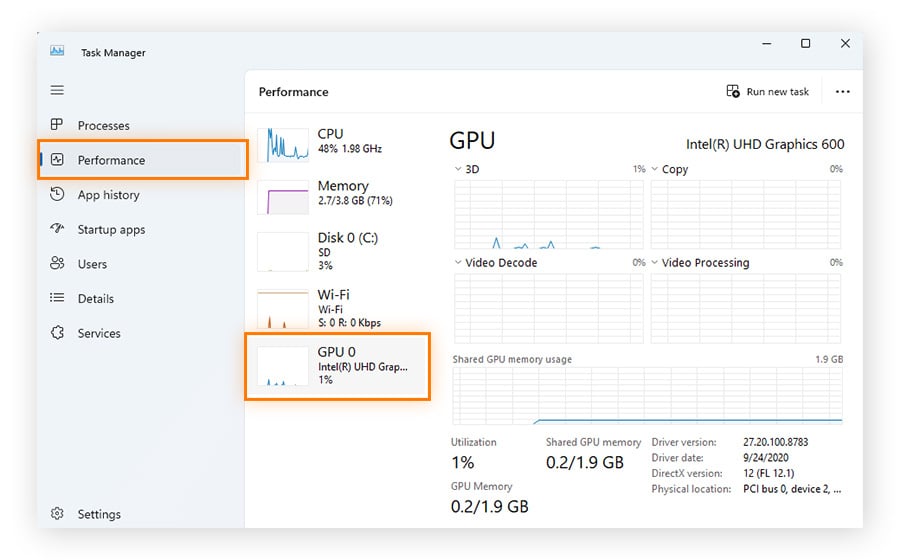
Along with displaying the graphics card that houses your GPU, Task Manager will show other details like GPU utilization (how hard your GPU is working at the moment) and GPU temperature to let you monitor its health. If you want to get more power out of your graphics chip, check out our guide to overclocking your GPU.
DirectX Diagnostic Tool
To check your video card, you can also use Windows’ built-in DirectX Diagnostic Tool, which troubleshoots video and sound-related hardware problems. Here’s how:
-
Type dxdiag into the desktop search bar and hit Enter to run the command.
-
Click the Display tab for a full rundown of your graphics devices, as well as the graphics drivers that run them.
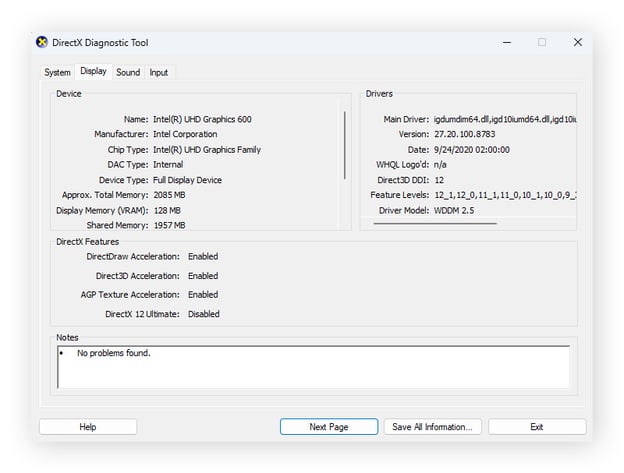
Any problems discovered by the checker tool will be detailed in the Notes box at the bottom of the window.
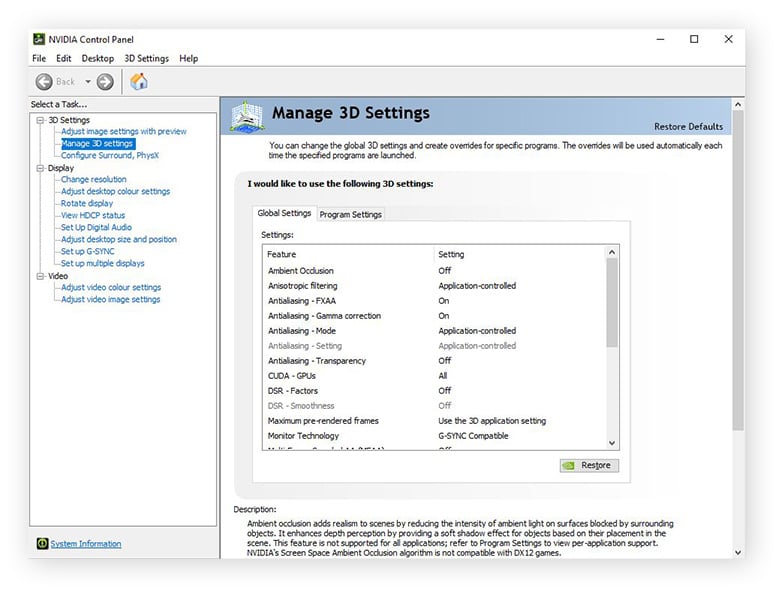
Control Panel
On the Windows Control Panel, you see what graphics card is installed on your PC. And if you’re using an NVIDIA display driver, you can also use the Windows Control Panel to launch a dedicated control panel to inspect system information and configure settings.
Here’s how to launch the NVIDIA Control Panel:
-
Right-click anywhere on your desktop. If you’re on Windows 11, you then need to choose Show more options.
-
Click NVIDIA Control Panel from the list of options.
-
When the NVIDIA graphics card control panel pops up, click System Information in the bottom-left corner.
The System Information window will appear, auto-detecting NVIDIA drivers, RAM memory, and displaying other details related to your graphics hardware.
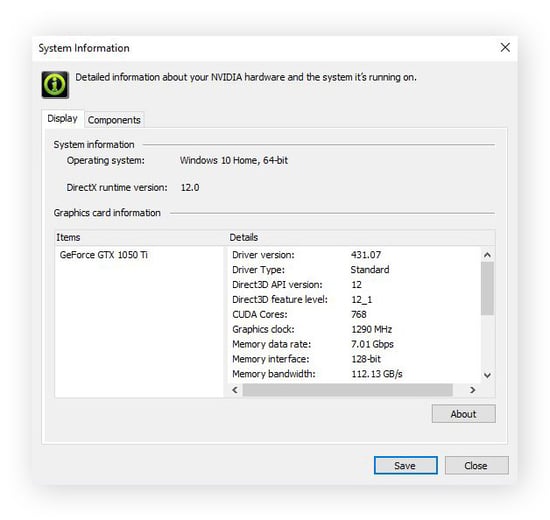
Like checking your GPU, checking your PC specs is another way to optimize Windows 10 for gaming. By understanding your hardware’s limits, you can boost your computer's performance with practices like overclocking your CPU — and you don’t have to mess with any screwdrivers or computer slots!
What is a graphics card (GPU)?
Although often used interchangeably, GPUs and graphics cards are not the same. Also called video cards, display adapters, or graphics adapters, graphics cards generate and feed images to a computer’s display or monitor. To do so, graphics cards contain various components, including a GPU, or graphics processing unit.
The GPU is the nerve center of the graphics card, where the necessary processing to display images takes place. Having fetched texture data from the graphics card memory, the GPU performs rapid calculations to process the data. Once processed, the data is sent back to the RAM before being sent to your screen where it appears as an image or a frame in an HD video or computer game.
GPU glossary
When checking your GPU’s capabilities, you’re likely to run into some unfamiliar terminology. But don’t fret, we’ve got you covered!
Here’s a glossary of GPU terms to help you assess your GPU:
-
Clock speed: Clock speed refers to the speed at which a GPU’s core operates to render graphics. It’s typically measured in MHz or GHz. A GPU boost clock refers to the maximum frequency a GPU can operate normally — in other words, its peak performance.
-
FPS: Frames per second or FPS refers to the number of images, or “frames,” rendered by your GPU and displayed on the screen per second. FPS is used as a metric to measure how smoothly a game or app is running. The higher the FPS, the smoother the rendering.
-
GDDR: Graphics Double Data Rate or GDDR is a type of high-speed video memory that’s used to store and access graphical data in a GPU. There are different types and versions of GDDR, some offer better video rendering performance than others.
-
Resolution: Resolution refers to the number of pixels displayed on a screen. Higher resolutions generally require more GPU power to render each frame.
-
TDP: Thermal Design Power or TDP refers to the theoretical maximum amount of heat a GPU or CPU can generate under a given workload. This is an important metric when considering GPU cooling solutions.
-
VRAM: Video Random Access Memory or VRAM is used to store and manipulate graphical data on your GPU. It’s key for displaying high-resolution textures, complex 3D models, and smooth rendering. Ultimately, it’s like RAM for your GPU.
Get sharper graphics with Avast Driver Updater
No matter how powerful your GPU or how much video RAM you’ve got to spare, your graphics card is only as good as the drivers running it. Outdated or buggy software can result in crashes, laggy gameplay, reduced FPS, and low-quality graphics textures.
That’s why keeping your drivers fully optimized with a world-class driver updater is vital for ensuring optimal performance.
With Avast Driver Updater, it’s not just your graphics drivers that benefit from automatic detection, repairs, and updates — it’s all of them. Along with crystal clear images and silky smooth video rendering, Driver Updater unlocks peak performance across your entire PC. Get fewer freezes, richer audio, and faster browsing.
FAQs
How do I check my graphics card on Windows?
To check your graphics card performance on Windows 10 and Windows 11, launch the Task Manager app from the Start menu. Under the “Performance” tab, select the GPU option to view a detailed summary of your graphics card performance metrics such as current memory usage and GPU temperature. If your graphics card is maxed out, overclocking your GPU can help to increase performance.
How do I check my NVIDIA graphics card?
You can check your NVIDIA graphics card in a laptop or desktop by opening System Information via the Start menu and checking the “Display” tab. Alternatively, if an NVIDIA driver is installed on your computer, you can open the NVIDIA Control Panel to view your GPU information or update your drivers to boost performance.
How do I check my RTX graphics card?
To check an RTX graphics card, or any other type of NVIDIA or AMD GPU, go through the Start menu and check the GPU section under the Task Manager “Performance” tab, or look under Display Adapters in the Device Manager utility. You can also use the NVIDIA Control Panel to check RTX system information.
Why isn't my graphics card showing up?
There could be several reasons why your graphics card isn’t being detected. To troubleshoot the issue, try uninstalling and reinstalling your graphics card drivers and updating Windows to the latest version. Then, check if your GPU is correctly inserted in the right slot of your computer before disabling and re-enabling your graphics card. If you’re still having trouble, contact your graphics card manufacturer for help.